Addressing big data challenges in healthcare is pivotal for realizing the industry's data-driven future.
Electronic health records , medical imaging, and the growing use of connected medical devices generate vast amounts of information. This data can revolutionize healthcare by enabling personalized medicine, improving diagnosis , optimizing treatment plans, and driving medical research.
To truly harness this potential, robust data management and analysis strategies that ensure the integrity, privacy, and accessibility of health information are crucial.
This article explores the six significant data challenges in healthcare. By acknowledging and comprehensively understanding these hurdles, we will be able to develop the most effective strategies to unlock and fully appreciate the transformative impact of big data on healthcare.
Future outlook
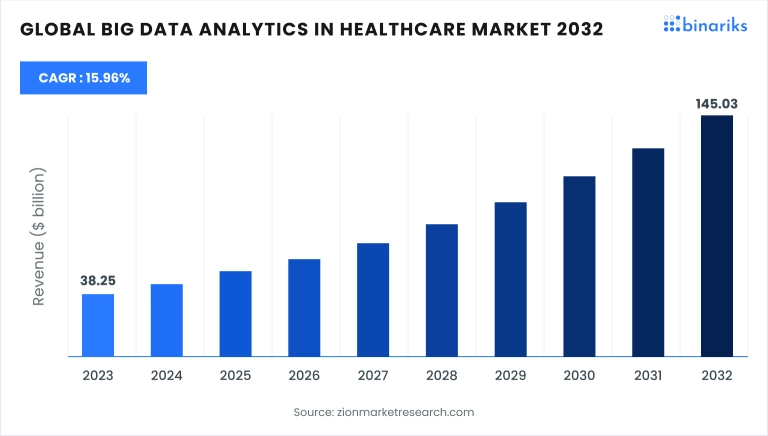
In 2023, the market value for big data analytics in healthcare was estimated at around $38.25 billion. It is projected to experience substantial growth, reaching approximately $145.03 billion by 2032. This growth trajectory suggests a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 15.96% from 2024 to 2032.
In terms of geography, North America dominated with the largest revenue share. The key market player in the region is primarily focused on developing and commercializing advanced streaming analytics for both residential and commercial applications.
Factors likely to drive the growth of the regional streaming analytics market include an increase in per capita income, an innovative population, and the continued adoption of emerging technologies for individual and commercial applications.
Furthermore, the Asia Pacific region is anticipated to experience a high CAGR in the global market. The rapid increase in revenue from smartphones and tablets, enhanced consumer IoT device adoption, and higher disposable incomes in economies are significant factors propelling the regional market's growth. With improved internet connectivity, companies can now develop and deploy advanced IoT sensors and devices for process controls.
Market dynamics shows that even the healthcare big data challenges we are going to explore further cannot overshadow the immense potential this technology holds. By acknowledging these hurdles and developing effective solutions, we can pave the way for a future where big data becomes a transformative force in healthcare.
This is all about the world where:
- Personalized medicine gains momentum, with treatment plans tailored to the patient's unique genetic makeup and medical history.
- Early disease detection is significantly improved, allowing timely intervention and potentially life-saving outcomes.
- Healthcare delivery is more efficient through optimized resource allocation and streamlined processes informed by data-driven insights.
These are just a few glimpses into the perspectives of big data in healthcare . As we delve into the transformative impact big data can have on patient care, we are also poised to explore the risks of big data in healthcare.
Unlock your data's potential: discover Binariks' Big Data and analytics services today!
6 major challenges of healthcare big data
6 major challenges of healthcare big dataExploring the intersection of big data and healthcare problems reveals critical barriers to leveraging technology for improved patient outcomes.
1. Data quality and integration
One of the most common problems with big data in healthcare is that medical records from different hospitals, clinics, and laboratories may not follow standardized formats. This inconsistency makes integrating data from disparate sources difficult, creating a fragmented picture of a patient's health.
Furthermore, missing or erroneous information in medical records can also significantly impact the accuracy of data analysis and the reliability of insights derived from big data.
Penn Medicine, an academic medical center, employs predictive analytics to reduce risks for critically ill patients through palliative care. In 2017, they introduced the Palliative Connect trigger system, which utilizes a machine learning algorithm to analyze patients' Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and predict potential risks. This system alerts clinicians, allowing proactive responses to patients' needs.
Pilot testing revealed a 74% increase in consultation rates, with 57% of triggered consults approved by the control expert team, demonstrating the effectiveness of predictive analytics in enhancing patient care.
In this case, integrating data from various sources (electronic health records, medications, social determinants) to accurately assess a patient's suitability for palliative care can be challenging due to inconsistencies in how data is collected and stored across institutions (Source ).
2. Data privacy and security
Information sensitivity is one of the challenges of big data in healthcare, dramatically affecting its successful implementation. Striking a balance between leveraging data potential and protecting patient confidentiality is crucial.
The vast amount of patient data creates a target for cyberattacks, so the following security measures must be implemented to safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access:
- Encryption of data: Ensuring data is unreadable to unauthorized users by encrypting information both at rest and in transit.
- Access controls and authentication: Implementing mechanisms to limit data access to authorized personnel only, including secure authentication methods to verify identities.
- Regular security audits and compliance checks: Conduct periodic evaluations to identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure adherence to industry standards and regulations, like HIPAA and GDPR.
- Secure, dedicated networks: Dedicated networks should be utilized for the transfer of patient data to reduce the risk of interception by cyber attackers.
- Advanced security measures: Adopting additional sophisticated security strategies to protect patient data from cyber threats and maintain confidence in healthcare systems.
3. Data standardization issues
Standardization is also one of the big data challenges. Standardized formats ensure consistent data collection and facilitate seamless analysis across various healthcare systems.
Imagine a scenario where one hospital records blood pressure readings in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) while another uses kilopascals (kPa). Standardized formats would eliminate these discrepancies, allowing for more accurate comparisons and better prediction models.
For instance, in collaboration with HP Autonomy, Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital (LPCH) created an analytical platform using the IDOL engine to handle unstructured healthcare data. With over 400 connectors, it provides medical workers access to insights from various clinical systems through a dedicated interface.
Despite integrating the analytical system into daily operations at LPCH, none of the developed ML algorithms were used because of data inconsistency (Source ).
4. Data storage and transfers
No wonder, among the existing big data problems in healthcare is one concerning the sheer volume of data generated, which can strain existing storage infrastructure.
Finding cost-effective and scalable storage solutions is a key to survival in the business. Also, securely transferring large datasets between healthcare institutions can be complex and time-consuming. Efficient data transfer protocols are needed to facilitate data sharing and collaboration.
For example, the University of Chicago Medical Center tackled operating room delays by addressing challenges in managing healthcare data.
The vast volume of data strains storage infrastructure, necessitating cost-effective solutions. Securely transferring large datasets between institutions is complex and demands efficient collaboration protocols. By leveraging a large volume of real-time data, predictive analysis, and machine learning, the hospital reduced turnover time by 15-20%, achieving a $600.000 annual revenue increase (Source ).
5. Data structure issues
The sheer volume of data generated within healthcare systems is staggering: patient records, medical images , genomic data, and more. Managing this information requires a robust infrastructure to store, process, and analyze data efficiently.
However, healthcare data's complexity often surpasses traditional IT infrastructures, demanding scalable solutions capable of handling exponential growth.
For instance, EHRs often contain unstructured data, such as physician's notes, that are difficult to analyze and integrate with structured data like lab test results.
In addition, the same EHR might be stored as an XML document, where certain elements are clearly defined (such as patient name, ID, and birth date), while others can vary widely in format (such as physician notes or clinical observations). This is called semi-structured data. Its complex nature allows for flexibility in documenting healthcare information but also presents data processing and analysis challenges.
Unlike fully structured data that fits neatly into a database (such as blood pressure readings, vital signs, medication prescriptions, billing or clinical codes, and lab results mentioned above), semi-structured data requires more sophisticated parsing and interpretation to extract meaningful information.
6. Infrastructure and scalability
The sheer volume of data generated within healthcare systems is staggering: patient records, medical images, genomic data, and more. Managing this information requires a robust infrastructure to store, process, and analyze data efficiently.
However, the complexity of healthcare data often surpasses traditional IT infrastructures, demanding scalable solutions capable of handling exponential growth.
Here are three key issues healthcare companies have today:
- Limited storage capacity: the challenge of accommodating the ever-increasing volume of data necessitating scalable storage solutions.
- Computational limitations: the need for more powerful computing resources to process and analyze large datasets effectively.
- Data processing delays: the efficiency challenges in managing and processing data, underscoring the importance of optimizing data processing workflows.
How to overcome these issues
These six major challenges of using big data in healthcare we've identified present significant roadblocks, but they are not insurmountable. By implementing a multipronged approach at both the micro and macro levels, and leveraging various technologies in synergy with big data, the healthcare industry can handle most of the problems.
Optimizing patient care:
- Enhancing data quality: Standardize data formats (HL7 FHIR) and use data cleansing tools to ensure accurate patient information.
- Empowering patients: Implement user-friendly consent management platforms to give patients control over their data.
Advancing research and public health:
- Breaking down data silos: Establish secure data repositories for controlled data sharing and leverage cloud computing for scalable storage and analysis.
- Safeguarding data on the move: Utilize secure data transfer protocols (HTTPS) to ensure data privacy during transfer between institutions.
Synergy
Standardized data allows for seamless integration and analysis across institutions. Secure access controls and data transfer protocols safeguard privacy while enabling collaboration. NLP and machine learning unlock the hidden potential within unstructured data, leading to groundbreaking discoveries. As you can see, many technologies used in synergy with big data create a powerful ecosystem.
For example, Agilon Health, using telehealth and big data, showed superb effectiveness during the ongoing global health crisis. The organization utilized the Health Catalyst Data Operating System (DOS) platform to analyze COVID-19 data from Italy, China, and the US, creating a mortality model.
Within a week, risk scores were assigned to 125.000 individuals, with the team reaching nearly 50% of the patient base, focusing on older age groups for precautionary measures. In response to the pandemic, Agilon Health swiftly transitioned medical appointments to telehealth channels, resulting in a partner location increasing telehealth appointments from zero to 2.200 in weeks 12 and 13, aligning with social distancing measures and pandemic policies (Source ).
By working together, these technologies can unlock the true power of big data in healthcare , paving the way for a future of personalized medicine, improved public health initiatives, and a healthier world.
Web and mobile engineering services for the healthcare provider We solved our client's compliance and big data challenges, enabling them to cut infrastructure costs, scale, and expand outreach.
Read more
Web and mobile engineering services for the healthcare provider
We solved our client's compliance and big data challenges, enabling them to cut infrastructure costs, scale, and expand outreach.
Conclusion
While the limitations of big data in healthcare remain, its potential is undeniable. By implementing effective strategies, we can unlock the true power of big data and usher in a new era of healthcare.
Binariks offers a full range of services that meet healthcare organizations' needs and goals. We can help you implement industry-standard data formats , ensure data accuracy and privacy, leverage advanced analytics and artificial intelligence , and manage big data with scalable cloud solutions .
By partnering with Binariks, you gain a valuable ally with expertise in both big data and healthcare. Our team is ready to help you achieve tangible results and catalyze business growth.
Let's make it happen together. Contact Binariks today to see how we can transform your healthcare organization.
Share

