Healthcare continues to be one of the biggest targets of cyberattacks. Ransomware attacks alone increased by 328% in healthcare in the past year (source ).
Within this context, the rise of connected medical devices collecting massive volumes of data goes hand in hand with the increasing sophistication of cyber threats in this specific sector.

And even though this disturbing trend cannot outweigh all the benefits of connected devices and other innovative solutions in healthcare, it surely makes cybersecurity the top priority for the medical device market.
According to the GlobalData forecast, security for medical devices spending is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.3% in the coming years, from $869 million in 2020 to $1.2 billion in 2025 (source ).
In this article, we will consider primary regulatory guidelines and practices behind an effective medical device cybersecurity strategy.
Why ensure cybersecurity
The importance of cybersecurity for medical devicesTechnological innovations in healthcare have greatly improved patient outcomes and operational efficiency. But at the same time, they have created new risks that shouldn't be underestimated.
Whenever a medical device is driven by software, this software can be susceptible to cyber threats.
Medical device cybersecurity issues can have various negative consequences, including data theft and cyber extortion. And in the worst-case scenario, an attacker could gain control of the device, posing a serious threat to a patient's health and life.
However, even if patients emerged unscathed from a cyber attack, reputational damage for healthcare providers and medical device manufacturers is inevitable.
Therefore, it is essential to implement robust security measures. In other words, the best strategy is wherever possible to prevent cyber attacks on medical devices rather than deal with the aftermath.
Medical device security threats
Common threats to medical device cybersecurity
Like in other computer systems, cybersecurity risks in medical devices continuously evolve and come in all shapes and forms.
The most common medical device cybersecurity threats which are a cause of concern for the healthcare industry include:
- Malware: Malware can potentially compromise the functionality of a medical device. In particular, malware attacks can result in stealing or corrupting sensitive patient data and incorrect diagnoses or treatment recommendations.
- Data breaches: Medical devices can store sensitive patient data, including medical history, treatment plans, and personally identifiable information (PII). Even a single data breach would jeopardize not only patients' privacy and reputation but also physical safety.
- Ransomware attacks: In a ransomware attack, an attacker gains control of a medical device, SaMD, hospital network, etc., encrypts the files, and demands a ransom to restore access to them. This type of attack can prevent medical professionals from timely accessing critical patient data, delay care, and harm patients. Besides, encrypting files can damage them, potentially causing devices to malfunction, incorrect diagnoses, incorrect dosages of medications, and other health risks.
- DDoS attacks: A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is a type of cyber attack that floods the bandwidth or resources of a targeted system so that it cannot respond to requests. DDoS attacks can affect the functionality of connected medical devices, potentially causing serious harm to patients. For instance, a DDoS attack on a connected insulin pump could cause a delay in insulin delivery or an overdose, leading to life-threatening consequences.
- Cryptojacking: Cryptojacking occurs when an attacker uses a device's processing power to mine cryptocurrency. Although they may seem quite harmless compared to other cyber threats, these attacks can harm the device's functionality and shorten its lifespan.
- Phishing: Phishing is one of the most prevalent cybersecurity threats to medical devices, as that is how most cybercrimes begin. These attacks typically use emails to trick users into opening malicious links, thus giving away sensitive information or installing malware. Phishing emails and messages often reference reputable medical organizations to incentify link clicking.
Regulatory framework
Regulatory framework for medical device cybersecurity
The regulatory framework for medical device security contains various requirements to guide manufacturers in building secure and safe medical devices.
In the US, the key regulations pertaining to the cybersecurity of medical devices are provided by FDA guidance documents and international standards such as IEC 62304, ISO 14971, and ISO 27001.
IEC 62304
IEC 62304 was initially developed for SiMD (software in a medical device ) but is also applicable for SaMD (software as a medical device) and some medical apps.
This international standard establishes requirements for the entire software development lifecycle. This includes planning, design, development, testing, and maintenance.
IEC 62304 defines three software safety classes (Class A, B, and C). Based on this classification, it outlines the processes and documentation needed to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the software, including cybersecurity requirements (source ).
ISO 14971
ISO 14971 is a standard for managing the risk associated with medical devices (source ). It outlines a comprehensive process for identifying, analyzing, evaluating, and controlling potential hazards related to the use of medical devices throughout their lifecycle. This includes energy, chemical, performance-related hazards, and threats to medical device cybersecurity.
This standard helps manufacturers to establish a risk management process appropriate for their specific product and integrate it into their overall quality management system.
ISO 27001
The ISO 27001 standard is a widely recognized international framework for information security management. It provides a systematic approach to managing and protecting sensitive information.
In the context of connected medical devices, ISO 27001 is used to protect personal health information, secure communication networks, and maintain the confidentiality and integrity of patient data.
Compliance with this standard can help manufacturers to enhance cybersecurity for medical devices and achieve cyber-resilience (source ).
Become FDA/DiGA/MDR approved
Learn what regulations apply to your product in the EU and US

FDA, cybersecurity & medical devices
What the FDA says about cybersecurity for medical devices
The US Food and Drug Administration states that ensuring healthcare cybersecurity for medical devices is a shared responsibility of manufacturers, hospitals, and facilities.
Along with other government agencies, such as the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the US Department of Commerce, the FDA regularly issues relevant cybersecurity guidances, whitepapers, and reports (source ).
And if some vulnerability is detected in a software or medical device, the FDA issues so-called "safety communications." These are specific recommendations the patients and healthcare providers should implement to minimize the potential risks.
Precise requirements of the FDA and medical device security regulations largely depend on the type of device or software. Yet, in short, regulators' key demands and expectations of the manufacturers include:
Addressing cybersecurity risks
Medical device manufacturers must comply with quality system regulations (QSRs). This part of federal regulations requires that medical device manufacturers identify, assess, and address risks. They must consider the impact on patient safety and the potential for unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Detailed recommendations for meeting QSRs would be found in the premarket and postmarket cybersecurity guidance (source ).
Providing cybersecurity information to users
Manufacturers should provide users with information on how to maintain the cybersecurity of their devices. For example, instructions on updating software and changing default passwords.
Reporting cybersecurity incidents
Manufacturers should report any cybersecurity incidents or vulnerabilities to the FDA on time and work to address them promptly.
Collaborating to increase cybersecurity
Manufacturers are supposed to participate in ISAOs (Information Sharing and Analysis Organizations) to share any crucial information on potential or emerging threats and problems with the FDA.
Such collaboration helps permanently improve medical device cybersecurity standards and protect patients.
Maintaining documentation
Manufacturers should maintain relevant documentation on their cybersecurity risk management practices and the measures they have implemented to address identified risks.
Overall, the FDA's focus on cybersecurity reflects the importance of protecting patient safety and ensuring that medical devices continue to function as intended in the face of evolving cyber threats.
AWS-based Primary Care Platform
Binariks helped scale a web platform for patient monitoring and management
Cybersecurity best practices
To improve medical devices security, manufacturers and healthcare providers can adhere to the following practices:
- Secure design principles: Manufacturers should follow secure design principles. This may include implementing strong authentication and access controls, encrypting sensitive data, and building mechanisms for detecting and responding to security incidents.
- Network segmentation: The performance and security of medical devices and healthcare facilities can be improved by implementing network segmentation. This involves separating medical devices from other parts of the network and restricting access to only authorized users and devices.
- Patch management: Medical device manufacturers and healthcare providers need to implement effective patch management. Briefly, security patch management is the process of regular and timely updating of systems and software by inserting code to fill in (to patch) the vulnerability.
- User training: Healthcare facilities' employees and end users are often the weakest links in the security chain. That is why it is essential to enhance their data privacy awareness on an ongoing basis. Access control policies and multi-factor authentication are helpful, but training medical device users to identify and avoid security breaches is no less efficient.
- Monitoring and incident response: Healthcare providers should implement monitoring and incident response processes to quickly detect and address any cybersecurity incidents quickly.
And as for vital security measures in the course of medical device software development, the secure SDLC is the answer.
The Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDLC) is a framework for integrating security activities into every stage of software development.
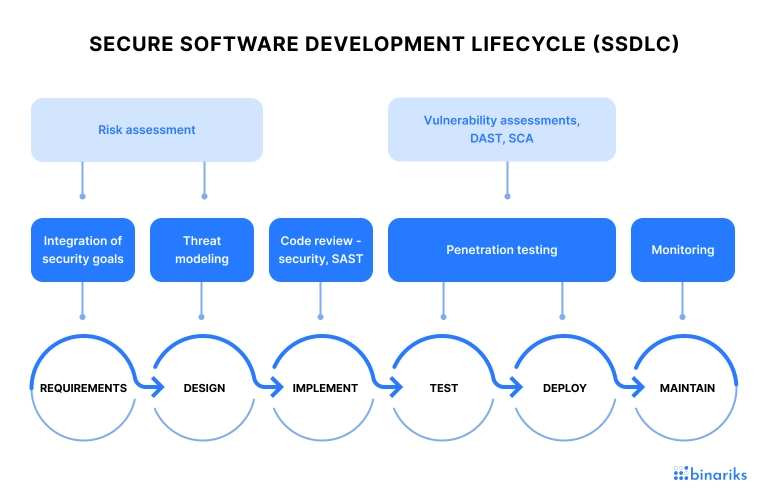
SSDLC typically includes the following stages:
- Requirements: Identifying security requirements and defining security objectives.
- Design: Designing software with security in mind, including threat modeling and risk analysis.
- Implementation: Implementing security controls and testing code for security vulnerabilities.
- Testing: Conducting security testing , including penetration testing and vulnerability scanning.
- Deployment and maintenance: Ensuring secure software deployment, including securely configuring devices and implementing effective patch management.
Binariks and safe medical devices
Binariks and safe medical devices
Binariks provides software development services for a wide range of industries, including healthcare.
The company ensures medical device and software cybersecurity by:
- following secure coding practices
- complying with regulatory standards, such as HIPAA, FHIR, and GDPR
- performing rigorous testing and security assessments
In particular, Binariks can develop custom software solutions that integrate with medical devices, securely collect and transmit data to cloud-based healthcare platforms, and provide analytics to healthcare professionals.
We also offer ongoing support and maintenance to ensure that the software stays up-to-date with the latest security patches and compliance requirements.
Want to become HIPAA-compliant? Learn about best practices of FHIR implementation.
 Read more
Read more

Binariks and safe medical devices
Binariks and safe medical devicesWant to become HIPAA-compliant?
Learn about best practices of FHIR implementation.

Final thoughts
Final thoughts
Cybersecurity is a crucial issue in the medical device industry. It is not only about damaged reputation and lost revenue but also the potential direct risks to the patient's health and life.
That is why cybersecurity measures must be planned from the beginning of medical device software development.
Contact Binariks if you need a reputable tech partner for creating secure medical device software. We make no compromise on cybersecurity and build сustom healthcare solutions in compliance with all the required industry standards.
FAQ
Share

