AI adoption is accelerating across industries, and AI-powered business process automation (AI BPA) – the application of artificial intelligence to automate repetitive, rule-based, and data-intensive business workflows – is becoming a central driver of operational scale.
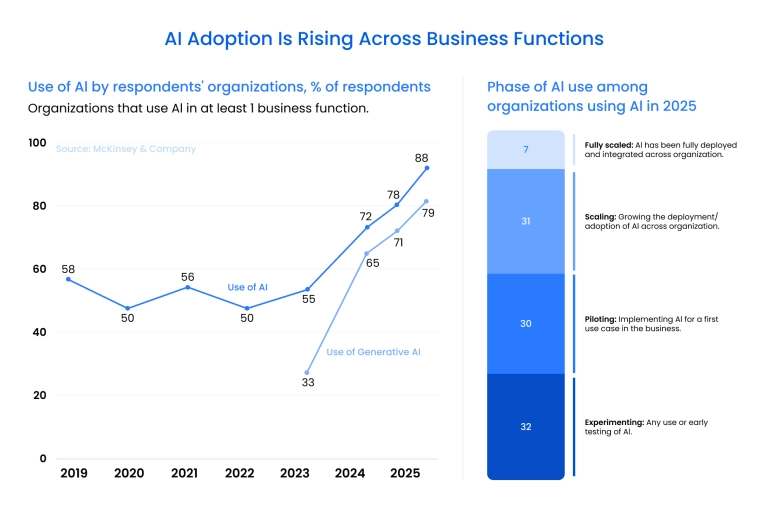
According to McKinsey's 2025 State of AI report, "88% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function, compared with 78% a year ago."
The shift reflects a broader trend: automation has evolved from a cost-reduction tool into a strategic capability that redesigns how value is created across workflows, teams, and entire business models.
The graph below shows how the use of AI has expanded sharply in the past years:
Organizations experiencing rapid growth face a predictable set of automation barriers. Manual data entry across multiple systems creates bottlenecks, document-heavy processes take hours rather than seconds, and quality control still depends on human review even when AI could preprocess the information. Meanwhile, hiring velocity cannot match operational demand growth – creating a structural constraint that only automation can resolve.
At the same time, scaling agentic automation – AI systems that autonomously execute multi-step workflows, make decisions, and adapt to exceptions without human intervention – remains rare. As shown in the chart below, no more than 10% of organizations report scaling AI agents in any single business function:

These adoption gaps reveal why forward-looking organizations now treat automation as a core strategic capability rather than an IT efficiency project.
Traditional robotic process automation (RPA) tools struggle with process variability – inconsistent invoice formats, multilingual customer messages, or contracts with irregular clause structures. AI-powered automation overcomes these limitations by interpreting unstructured data (PDFs, emails, images), orchestrating complex workflows across systems, and continuously learning from operational outcomes.
For organizations exploring enterprise automation , these capabilities unlock compounding operational value: faster cycles, fewer errors, and processes that scale without adding operational overhead.
Here's what you'll learn in this guide:
- Key differences between traditional BPA, AI-powered BPA, IPA, and emerging agentic automation
- How to identify high-value automation candidates and avoid processes where AI delivers low ROI
- The technology stack behind modern automation: OCR, NLP, ML, workflow engines, integrations
- Practical use cases across finance, HR, procurement, customer support, and operations
- A step-by-step implementation framework from assessment to scaling
- Common automation failures and how to avoid them
- How Binariks supports automation with process assessment, AI integration, and adoption support
If you're evaluating automation or planning to scale existing workflows, this guide will help you understand what works, what breaks, and how to build automation that delivers measurable impact.
What is AI-driven business process automation?
AI-driven automation expands the limits of traditional BPA by removing its dependence on strict rules and perfectly structured inputs. Classic automation works only when data arrives in uniform formats and processes follow predictable paths. The moment layouts change, exceptions appear, or information becomes unstructured, rule-based systems break down, which is why traditional tools remain confined to low-variation workflows.
AI-Powered BPA changes this dynamic. Through AI business automation, models interpret documents, extract entities, classify information, and validate data before it enters a workflow.
AI handles variability: different layouts, languages, data quality issues, and exceptions, which makes it suitable for processes like claims intake, contract processing, or customer request routing. This flexibility is the core advantage of business process automation with AI, where systems adapt rather than simply follow instructions.
This evolution leads to Intelligent Process Automation (IPA), where AI and RPA operate together. RPA runs structured steps, while AI manages the cognitive layer: reading, deciding, validating, and learning. This combination enables organizations to automate entire workflows rather than isolated tasks. Many teams rely on this approach when modernizing functions linked to AI in operations management .
Here's how the three models differ in practice:
- Traditional BPA: rule-based, structured, predictable;
- AI-Powered BPA: interprets unstructured inputs, manages variation, learns patterns;
- IPA: merges workflow automation with AI-driven decisioning.
The outcome is an automation layer that understands context instead of blindly repeating steps, enabling businesses to automate complex, decision-intensive processes that previously required constant human involvement.
From RPA to intelligent automation: The evolution
The automation landscape has shifted far beyond simple scripts and rule-based bots. What began as traditional RPA has now evolved into multi-layered, cognitive, and increasingly autonomous systems capable of managing complex, dynamic workflows.
This progression explains why companies exploring AI for business automation move from isolated task automation to full, end-to-end orchestration driven by learning systems.
The evolution process
RPA was built to automate structured, repetitive tasks – copying data between systems, triggering rule-based actions, or executing predefined workflows. It excels when nothing changes, and every input looks the same.
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) adds AI capabilities to RPA. Models classify documents, extract entities, validate information, and route exceptions, allowing automation to handle variation and unstructured inputs. IPA bridges the gap between traditional workflow automation and decision-based tasks.
Agentic Process Automation goes one step further. Instead of following a fixed script, agentic systems plan, execute, and adapt across multiple steps in a workflow. They break processes down into goals, interpret context, and coordinate actions dynamically, the core idea behind AI-automated business operations. These systems interact with multiple tools, trigger task chains, and adjust their behavior based on outcomes rather than just instructions.
Here are some practical examples:
- A traditional RPA bot moves invoice data from PDF to ERP.
- IPA reads any invoice layout, extracts line items, validates amounts against purchase orders, and routes exceptions.
- An agentic system proactively checks supplier history, investigates discrepancies, requests missing documents, updates finance records, and notifies stakeholders without predefined scripting.
Comparison table
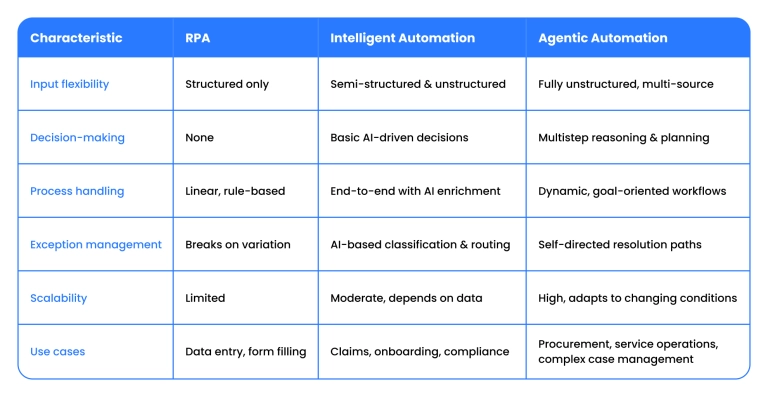
This evolution reflects where automation is heading: bots that no longer follow scripts, but understand processes, adapt to variation, and collaborate across systems to deliver outcomes, not just completed tasks.
Core technologies powering AI business process automation
Modern automation relies on a stack of technologies that work together to interpret data, make decisions, and execute workflows. Traditional tools could only follow rigid rules, but today's systems use AI to understand documents, classify information, predict outcomes, and coordinate multistep processes. This combination is what makes AI for business processes scalable; it connects cognitive insight with operational execution.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is the foundation of many processes, especially those involving emails, contracts, forms, and customer messages. Modern NLP models extract entities, classify intent, summarize documents, and validate information at scale. This allows systems to read unstructured text, identify what matters, and route or process it without manual review.
In high-volume environments such as claims intake or onboarding, NLP reduces cycle times by interpreting text in multiple languages, detecting anomalies, and turning raw content into structured data that downstream systems can use.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning models uncover patterns, predict outcomes, and make data-driven decisions inside workflows. ML powers risk scoring, lead prioritization, payment prediction, fraud detection, routing optimization, and eligibility assessment.
Because ML adapts over time, it continuously improves accuracy as more data flows through automated processes. This adaptability makes it ideal for AI-driven business process automation, where rules change, inputs vary, and exceptions can't be scripted manually.
Computer vision
Computer vision enables systems to "see" and interpret visual information, such as invoices, receipts, IDs, handwritten notes, and scanned documents. It extracts text, reads tables, detects signatures, flags discrepancies, and verifies document authenticity.
In use cases like invoice processing or KYC verification, vision models reduce manual review from minutes to seconds. They also integrate tightly with OCR and NLP pipelines, turning messy images into reliable, structured data that can be orchestrated through automation.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA handles structured, predictable actions: moving data between systems, triggering workflows, clicking through UI paths, and enforcing rules. Modern automation combines RPA with AI, allowing bots to operate on unstructured inputs, resolve exceptions, and take context-aware actions.
This hybrid model extends RPA beyond simple tasks, making it a key AI solution for business automation, especially when workflows include both cognitive steps (interpretation) and mechanical steps (execution).
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics evaluates patterns across historical data to forecast outcomes, detect anomalies, and anticipate operational issues. In finance, it predicts late payments; in HR, attrition risk; in supply chain, demand surges or inventory shortages.
These signals allow businesses to adjust processes proactively rather than reactively. When integrated into automated workflows, predictive models trigger actions automatically – rerouting tasks, adjusting SLA priorities, or alerting teams before problems escalate.
Generative AI & LLMs
Generative AI and large language models introduce a new layer of intelligence to automation. They can draft emails, fill forms, interpret policies, generate summaries, reconcile inconsistencies, or interact with users conversationally. LLMs also enable multistep reasoning, which allows systems to break tasks into smaller parts, plan actions, and adjust based on feedback.
Many organizations engage AI consulting companies to integrate LLM-driven agents into their service operations, knowledge management systems, or document-heavy workflows, creating automation that learns, explains decisions, and coordinates multiple steps autonomously.
All of these technologies work together to create automation that understands data, makes decisions, and coordinates actions end-to-end. Combined, they transform fragmented workflows into integrated, adaptive automation systems, shifting organizations from simple task automation to intelligent, self-improving operations at scale.
Why AI matters for business process automation
AI matters for automation because it handles the variation, volume, and complexity that traditional tools can't. As processes grow more data-heavy and decision-driven, AI becomes the only scalable way to maintain speed, accuracy, and cost efficiency. Let's check out some latest stats:
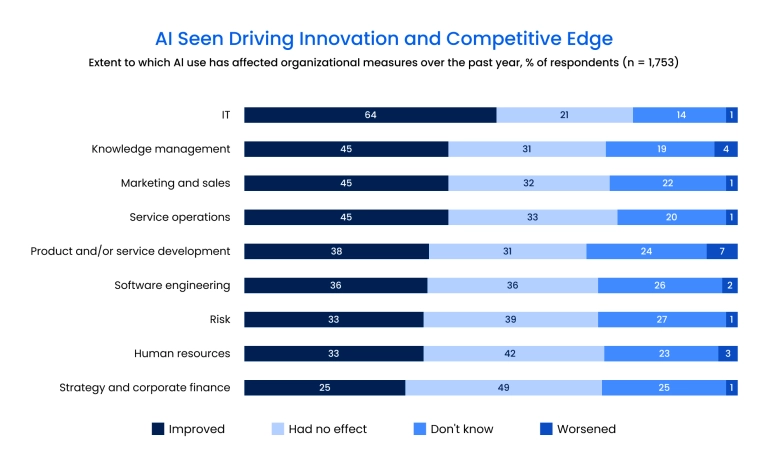
- Recent McKinsey data shows that AI delivers measurable improvements across key operational metrics, with the strongest gains in innovation, employee satisfaction, customer experience, and competitive differentiation.
- Another recent study on arXiv (2025) demonstrates the operational impact of integrating AI with business process management. In experiments across several enterprise scenarios, the model reduced processing time by 42%, improved resource utilization by 28%, and cut operating costs by 35% . The system also maintained 99.9% availability under high concurrent loads, showing that AI-enhanced workflows can scale reliably even in complex, high-volume environments.
- Also, according to Ardem, companies combining AI-driven automation with document processing and workflow orchestration see processing times drop by up to 50% , compliance costs reduced by 30%, and a sharp reduction in manual errors.
Key advantages of AI-powered automation
- Cost reduction and operational efficiency – automation lowers labor-intensive work and reduces error-related costs.
- Speed and scalability – AI handles large volumes of unstructured data rapidly, making high-throughput tasks viable at scale.
- Decision support and intelligence – beyond mechanical tasks, AI enables evaluation, classification, exception detection, and data-driven decisions.
- Flexibility and resilience – systems adapt to changing formats, varying inputs, and evolving business conditions, reducing dependence on rigid workflows.
Because of these benefits, many organizations now treat automation not merely as a productivity tool but as a strategic capability, and those that invest accordingly often unlock meaningful returns.
Where AI automates business processes: Top 5 use cases
AI is most effective where processes combine high volume, inconsistent inputs, and frequent decision-making. These conditions create bottlenecks for human teams but map naturally to data-driven automation.
Many organizations start with these areas because the benefits of business process automation are immediate: faster cycle times, fewer errors, and reduced operational load.
Customer support & service operations
AI classifies tickets, identifies intent, prioritizes urgent issues, and generates responses for common requests. In high-volume environments, this cuts handling time and reduces the need for manual triage. Models can also analyze sentiment, detect churn risk, and automatically escalate complex cases.
Finance & document-heavy workflows
Automation reads invoices in any format, extracts line items, validates amounts, and routes exceptions. Similar models process contracts, receipts, and compliance documentation, accelerating workflows that previously required manual review. This is often the first step in business process automation implementation for finance teams.
HR & employee onboarding
AI verifies documents, checks compliance, schedules training, and sets up access rights based on role. It also assists with resume screening, internal knowledge search, and first-line HR support through conversational agents.
Procurement & supply chain
AI validates purchase requests, checks supplier compliance, analyzes pricing patterns, and triggers approval chains. In supply chain operations, predictive models support demand forecasting, inventory planning, and anomaly detection across logistics networks.
Risk & compliance monitoring
AI scans transactions, communication logs, and contracts to detect suspicious patterns or policy violations. Instead of periodic manual audits, organizations gain continuous oversight, faster escalation, and more consistent compliance outcomes. Many teams implement this through specialized AI/ML development services , which can be very helpful.
Starting with these areas helps organizations establish early wins and build a foundation for broader automation across the enterprise.
AI automation implementation framework for businesses
Successful automation comes from following a structured, predictable delivery path. The framework below outlines how companies move from identifying opportunities to scaling stable, production-ready AI systems.
1. Assessment & discovery phase
Identify processes with high manual load, variation, and measurable impact potential. Map inputs, exceptions, systems, and data quality to confirm automation readiness and define clear success metrics.
2. Strategy & roadmap development
Prioritize use cases based on ROI, technical feasibility, and operational urgency. Build a phased roadmap that aligns automation goals with business objectives, data strategy, and existing system constraints.
3. Proof of Concept (POC)
Validate the AI model and workflow in a controlled, low-risk environment. Test data pipelines, extraction accuracy, exception handling, and integration paths to uncover hidden dependencies before scaling.
4. Full implementation & integration
Deploy the solution into production with stable pipelines, orchestration logic, and system integrations. Ensure the automation seamlessly interacts with ERPs, CRMs, databases, and custom platforms.
5. Adoption & change management
Prepare teams for new workflows, update procedures, and define ownership. Provide training for business users, establish escalation paths, and ensure automation augments rather than disrupts operational roles.
6. Monitoring, optimization & scaling
Track performance, accuracy, cost impact, and exception rates. Implement model monitoring, retraining cycles, and continuous improvement loops to expand automation into adjacent processes once results stabilize.
Key challenges & how to overcome them
AI automation rarely fails because of the technology; it fails because organizations underestimate the operational realities around data, processes, and people. These are the most common blockers and how to neutralize them.
- Unstructured, low-quality data – Most enterprise workflows rely on messy, inconsistent, siloed data.
Fix: Early data cleanup, standardized formats, and strict validation rules.
- Processes that aren't truly standardized – Teams think they follow one workflow, but actual operations include dozens of exceptions.
Fix: Map the real process using interviews, logs, and shadowing before building automation.
- No clear internal ownership – AI initiatives stall when no one maintains models, handles exceptions, or updates workflows.
Fix: Assign process owners, automation champions, and explicit accountability.
- Stuck in "POC limbo" – Many companies run pilots forever without scaling.
Fix: Design with production in mind from day one: integrations, security, monitoring, retraining.
- Team-level resistance to change – Employees worry automation will disrupt workflows or reduce autonomy.
Fix: Involve users early, communicate benefits clearly, and position automation as augmentation.
In short, AI automation succeeds when data is clean, processes are real (not idealized), ownership is defined, pilots are built for production, and teams are brought into the change early.
Common AI automation mistakes to avoid
- No clear problem definition. Teams jump into models before agreeing on a measurable business goal; define the specific process bottleneck and success metrics upfront.
- Automating broken processes. AI won't fix inefficient workflows; streamline and document the process before applying automation.
- Poor data foundations. Dirty, inconsistent, or siloed data kills performance; invest early in data cleaning, pipelines, and governance.
- Ignoring people and change management. Employees resist new workflows when they’re uninformed; communicate early, train teams, and include process owners from the start.
- Skipping post-launch monitoring. Models drift, integrations break, processes evolve; set up continuous monitoring, retraining, and feedback loops.
How Binariks supports AI-powered business process automation
Modern enterprises don't need another vendor; they need a partner who understands the operational bottlenecks, aligns automation with business goals, and builds AI systems that actually work in production.
This is where Binariks stands apart. Our team blends AI engineering, architecture, and domain expertise to help organizations redesign their processes around reliability, speed, and scale, not just deploy isolated models.
Instead of just offering AI tools, we help clients evaluate where automation delivers the highest ROI, validate feasibility with real data, and implement solutions that remain stable under real-world load.
Our approach is grounded in measurable outcomes and transparent delivery. We work shoulder-to-shoulder with stakeholders across operations, engineering, and compliance.
A practical example: From 3 hours to 15 minutes – AI-driven claims automation for a global risk management firm
One of the clearest illustrations of this partnership approach is our work with a global provider of risk management and corporate intelligence . Their Australia-based team faced a severe operational bottleneck: every client request arrived via email and had to be manually transcribed into TrackOps.
With 20-30 document formats, constant layout variations, and high-accuracy requirements, this workflow consumed hours daily and created scaling limits.
Binariks designed and implemented a fully automated, serverless AI pipeline that eliminated the bottleneck.
The results speak for themselves:
- 80-90% reduction in manual intake effort as the AI system now handles most claims end-to-end.
- Turnaround time dropped from 2 to 3 hours to under 15 minutes, unlocking true real-time responsiveness.
- 85-90% parsing accuracy, validated against historical data and guarded by confidence thresholds.
- Infrastructure cost kept around ~$2K/year, proving that automation at scale doesn't have to be expensive.
- 1,000+ documents/month processed reliably, across ~20–30 unique layouts and multiple file formats.
- Full audit trails, dashboards, and fallback workflows ensure compliance, visibility, and operational continuity.
This project demonstrates the core value Binariks brings:
- We solve the real operational problem, not just build a model
- We design for low-latency performance, governance, and scalability from day one
- We treat automation as a business transformation, not a tech experiment
- We deliver AI systems that are observable, secure, maintainable, and cost-efficient
- We stay engaged, from discovery to deployment to continuous optimization
If your organization is exploring or scaling AI-powered business process automation, Binariks is the partner that can help you cut through the noise, define where AI drives meaningful impact, and deliver production-grade solutions with measurable ROI.
Conclusion
AI-powered business process automation is no longer about isolated efficiency gains. For modern enterprises, it has become a structural capability that determines how fast operations scale, how resilient workflows remain under pressure, and how effectively teams handle complexity without adding headcount.
Organizations that succeed treat automation as a system, not a tool: grounded in real processes, supported by clean data, governed for reliability, and designed for continuous improvement. Those that don’t often stall in pilot phases or automate tasks that never move the business forward.
Binariks helps enterprises move beyond experimentation by designing and delivering AI automation that works in production, aligns with operational reality, and delivers measurable ROI. For organizations ready to scale automation responsibly, the opportunity is no longer whether to adopt AI, but how to build it right from the start.
Share

