If you're leading a healthcare organization, you're likely wrestling with persistent challenges that resist even the most sophisticated strategies:
- Rising costs that strain your budget regardless of efficiency measures
- Clinical burnout as your staff buckles under overwhelming workloads
- Critical shortages of qualified clinical personnel
- Outdated legacy systems that hinder rather than help your operations
Without a working resolution strategy, organizations can quickly become overwhelmed.
What's particularly striking is that many of these challenges aren't rooted in medical treatment but in the internal operational processes that support healthcare delivery. Yet, these matters have a lasting impact on physicians and patients alike.
For example, primary care physicians spend an average of 36.2 minutes per 30‑minute visit on EHR tasks, including roughly 6 minutes of "after hours." Doctors spend more time in the EHR than with patients, and over 60 percent of physicians report at least one symptom of burnout driven by administrative workload and inefficient workflows.
The goals seem unreachable in the constant rush to provide the best possible care at less cost, but there is a solution.
Optimization of clinical workflow in healthcare is crucial to keep organizations afloat and physicians functional and motivated in the face of these issues.
By focusing on the operational and administrative processes that run behind the scenes, modern technology can solve many workflow bottlenecks without interfering with actual medical decision-making.
This article reveals:
- The key aspects of clinical workflow management in healthcare
- How the assessment and automation of these workflows greatly improve them
- How workflow optimization can save hospitals $100,000-140,000 annually while reclaiming 2-4 hours of productive time daily
- An actual AI-based clinical workflow optimization project we worked on as an example
AI that delivers, not just promises. Partner with Binariks for AI automation you can trust.
What is clinical workflow?
A clinical workflow in healthcare is a system of processes and tasks that support the delivery of patient care. The clinical workflow includes the structure of work (who does what and when), the flow of activities (how information and tasks move through a clinical setting), and the interactions between staff and staff, as well as staff and patients. Each healthcare professional's unique clinic workflow contributes to the overall care process. So, basically, various people work on various tasks simultaneously to achieve the best quality of care.
Here are the key components of a typical clinical workflow:
- Patient intake & identification
- Team coordination & communication
- Assessment & treatment planning
- Follow-up & care adjustment
- Documentation & data sharing
The technologies that support the typical clinical workflow are:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
- Mobile devices & computer stations
- Instant messaging between providers
- Clinical alerts & decision support systems
- Workflow automation tools
A typical medical workflow is typically delivered in four phases:
- Identifying patients in need of integrated care
- Engaging patients and building the integrated care team
- Providing treatment
- Monitoring outcomes and adjusting treatment plans
Types of clinical workflows
- Patient intake workflows
Includes initial registration, insurance verification, and data collection.
Example: A front desk clerk enters patient demographics into the EHR while verifying insurance coverage before a consultation.
- Diagnostic workflows
Include ordering tests, capturing the results, and interpreting findings to guide treatment.
Example: A physician orders bloodwork and an X-ray, which are reviewed before forming a diagnosis.
- Treatment workflows
Focus on delivering care: administering medication, performing procedures, or initiating therapy.
Example: A nurse gives antibiotics through IV, or a physiotherapist initiates rehab sessions based on the care plan.
- Discharge and follow-up workflows
Guide next steps aftercare: writing discharge instructions, planning home care, and scheduling follow-ups.
Example: A case manager schedules a follow-up visit and sends digital discharge notes to the patient.
- Care coordination workflows
Facilitate communication among providers to ensure continuity of care.
Example: A general practitioner consults a cardiologist and shares notes through a shared EHR system.
- Medication management workflows
Oversee prescribing, dispensing, and monitoring medications, including safety checks and adherence tracking.
Example: A pharmacist verifies dosages, checks for drug interactions, and updates the patient’s medication profile.
- Administrative workflows
Support operations through scheduling, billing, coding, reporting, and compliance-related processes.
Example: An automated system generates billing codes based on documented services and submits claims electronically.
- Emergency response workflows
Define rapid, protocol-driven actions in urgent scenarios (e.g., stroke alerts, trauma response).
Example: A Code Blue alert initiates a predefined response team protocol for cardiac arrest cases.
- Clinical documentation workflows
Standardize how patient information is recorded and accessed, typically through EHR systems.
Example: A nurse completes daily progress notes and vital signs directly into a tablet-based EHR interface.
- Telehealth and remote care workflows
Manage virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and digital patient communications.
Example: A doctor conducts a video consultation and orders a remote glucose monitoring plan for a diabetic patient.
How to assess clinical workflows
Before improving workflow in healthcare, it's crucial to understand how it functions, not just how it's supposed to.
Clinical optimization is impossible without a thoughtful workflow analysis in healthcare. Skipping this step risks automating inefficiencies or missing deeper structural issues in the clinical workflow in healthcare.
Proper clinical workflow assessments help identify the most common errors that repeat themselves over and over, assess the cost and quality of small workflow changes, and develop solutions that would actually work in the context of the specific healthcare organization.
A comprehensive assessment typically includes:
- Mapping current workflows: Visualize each care process step to see how tasks are performed and how information flows between people and systems.
- Identifying roles and responsibilities: Understand who performs each task, how responsibilities are handed off, and where coordination breaks down.
- Evaluating tools and technologies: Review how systems like EHRs, alerts, mobile devices, and communication platforms support (or hinder) workflow efficiency.
- Measuring time and resource use: Track how long tasks take, where delays happen, and how staff time and effort are distributed.
- Collecting feedback: Talk to frontline clinicians and staff to uncover workarounds, unmet needs, and pain points that might not be visible in the data.
Here are some of the ways to perform clinical workflow assessments:
- Watch clinical workflows unfold in live settings. Watch for any real-time deviations from documented procedures and bottlenecks that happen all the time.
- Conduct staff interviews or surveys. Aim to gather insights from everyone - nurses, physicians, and administrative staff. Different staff will have different experiences that contribute to the overall assessment.
- Use workflow mapping tools like flowcharts to outline each step and identify unnecessary complexity or gaps.
- Leverage EHR audit logs and tools to measure workflow efficiency and spot delays or underused resources.
- In time-motion studies, measure how long each task takes. Trained observers follow clinicians through their day and record the start and end times of each activity. This includes everything from direct patient care and charting to walking between stations or waiting for system responses.
- Use the method of computational ethnography: analyze existing digital records (like app usage or task completion timestamps) to identify workflow trends without manual observation.
- Use benchmarking: compare internal workflows to best practices in similar institutions to identify potential improvements. The organization you use in benchmarking should be the one that is successful at a particular task.
The most effective assessments combine qualitative insights from clinicians with quantitative data from systems and observations. This ensures that:
- You don't miss hidden human factors.
- You base changes on measurable evidence.
- Optimizations are both efficient and acceptable to staff.
Key challenges in clinical workflows
Below is the list of key challenges that can be solved by improving workflow in clinics:
1. Fragmented and siloed systems
Many healthcare organizations still rely on disconnected platforms that do not “talk” to each other. This makes it hard for teams to access a full patient picture in real time.
2. Manual and redundant processes
Manual data entry and redundant administrative steps add unnecessary friction to clinical workflows and drain time from patient-facing care.
3. Inefficient communication
Poor communication between departments and care teams is one of the biggest productivity drains in healthcare.
4. Lack of standardization
Without consistent processes across teams or facilities, clinical workflows in healthcare become fragmented.
5. Unstructured and inaccessible data
When patient data is stored in siloed or outdated systems, extracting meaningful insights or coordinating care effectively becomes difficult.
6. No built-in feedback or optimization loops
Many workflows are static and rarely revisited. Without routine assessments, problems go unnoticed, and systems fail to evolve with changing patient needs or organizational goals.
How to automate a clinical workflow
Automating clinical workflows requires a thoughtful approach that aligns technology with the particular needs of your healthcare organization. Here is how to optimize clinical workflows step by step:
1. Assess and map the current workflow
Before clinical workflow automation begins, thoroughly evaluate how the workflow currently operates:
- Identify repetitive tasks, manual data entry points, and bottlenecks.
- Map each process step and determine where delays or errors typically occur.
- Gather data-driven insights (e.g., time studies, EHR logs) and staff input.
2. Define automation goals
Set clear objectives:
- Are you trying to reduce the time spent on documentation?
- Improve patient throughput?
- Eliminate duplicated data entry?
- Enable real-time decision-making?
This step helps determine what should be automated and why.
3. Integrate with existing EHR systems
Automation is most effective when it seamlessly connects with Electronic Health Records (EHRs). This allows:
- Real-time access to patient data
- Automated data entry and updates
- Alerts and clinical decision support integrated into the care process
4. Leverage AI for intelligent process automation
Artificial Intelligence brings context-aware decision-making to automation:
- Computer vision: Detecting patient movements or procedural events (e.g., in surgical workflows)
- Predictive analytics: Flagging patients at risk or optimizing scheduling
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Automating clinical documentation or interpreting unstructured notes
- Chatbots or virtual assistants: Guiding patients through pre-visit questionnaires or follow-up steps.
- Agentic AI for healthcare : Agentic AI, unlike rule-based systems, can assess context, reprioritize tasks, and trigger follow-up actions without being explicitly programmed to do so.
5. Use RPA for repetitive administrative tasks
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is ideal for:
- Billing and coding
- Appointment reminders
- Insurance verification
- Data migration between systems
RPA bots mimic human clicks and keystrokes to reduce time spent on routine back-office work.
6. Ensure interoperability across systems
Automation must work across different platforms - lab systems, imaging software, scheduling tools, etc.
Use standard APIs and HL7/FHIR protocols to:
- Enable smooth data exchange
- Avoid data silos
- Reduce duplicate entry
7. Test with real users and iterate
Run pilots with actual clinical staff and iterate based on their feedback. Make sure that:
- The interface is intuitive
- The automation supports (not disrupts) their daily tasks
- AI recommendations are explainable and trustworthy
8. Monitor performance and optimize continuously
Track KPIs such as:
- Time saved per task
- Reduced errors
- Staff satisfaction
- Patient wait times
Use this data to fine-tune the automation logic and expand it to other processes.
Remember that some clinical workflows are suitable for automation while others are not.
The workflows suitable for automation include scheduling, admission and discharge processes, health records, documentation, inventory tracking, billing, reminders, triage routing, and data analysis.
Anything that involves complex diagnostics and human interactions is less susceptible to automation and can only be aided by it.
Common clinical workflow automations are:
- Automated appointment scheduling system
- A tool to automate the patient admission and discharge process
- Integration of EHR records with lab reports
- Automation of patient communication (call reminders, e-mails, in-app communication).
- Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) that help with establishing diagnosis and treatment
- Tools for onboarding new staff
- EDC in clinical research for streamlining clinical trial workflows
Binariks' expertise
At Binariks, we work with healthcare organizations to make their clinical workflows more connected and data-driven. Using our experience in AI, cloud technology, and system integration, we create solutions that go beyond just automation.
Our solutions help teams collaborate better with smarter decisions and truly patient-centered care.
We design custom healthcare software that:
- Automates time-consuming administrative and clinical tasks
- Integrates seamlessly with EHR and third-party systems using HL7/FHIR standards
- Provides real-time insights that enhance operational efficiency throughout care delivery
- Enables AI-driven decision support
- Enhances care coordination across multi-disciplinary teams and institutions
Leveraging ML and computer vision to enhance operating room efficiency
One of our key projects was with a surgical intelligence platform that supports collaboration and decision-making in the OR.
We helped develop a computer vision–based AI system using TimeSformer architecture that automatically recognizes four critical procedural milestones: patient entry ("wheels in"), operation start, operation end, and patient exit ("wheels out"), based on real-time video feeds.
The system processes video at 3-5 frames per second and achieves 95% accuracy in recognizing these key events.
This enabled the client's platform to capture accurate time-stamped data on operating room activity without manual input.
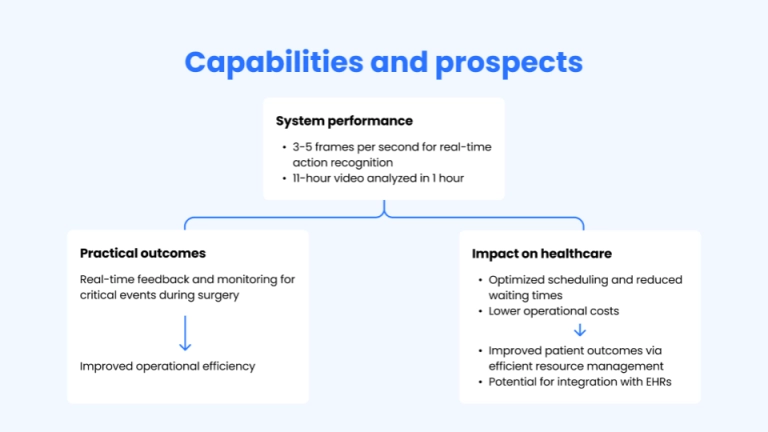
By making surgical workflows digitally observable, the solution allowed hospitals to:
- Track Operating Room Effectiveness (ORE) by comparing planned vs. actual procedure durations
- Improve the accuracy of surgical scheduling forecasts
- Reduce reliance on staff for manual documentation
- Optimize room utilization and staff allocation based on real-time OR usage patterns
![]()
The numbers speak for themselves: Implementing AI-powered OR scheduling technology can potentially bring $100,000-140,000 in annual savings per hospital through reduced labor costs alone.
Yet the operational gains are equally compelling. By automatically tracking OR activity and optimizing scheduling, hospitals can reclaim 15-30 minutes of idle time per OR daily. For an 8-OR facility, this translates to 2-4 additional hours of surgery time every day – time that can be used for more procedures, reduced patient wait times, or better work-life balance for surgical teams.
Consider the ripple effect: those extra 2-4 hours daily mean approximately 500-1,000 additional surgical hours per year. In a healthcare system where OR time is one of the most expensive and constrained resources, this efficiency gain can be worth hundreds of thousands of pounds in additional revenue and improved patient outcomes.
Moreover, beyond surgical applications, this same computer vision technology can be adapted for other healthcare monitoring scenarios:
- Patient bed monitoring – tracking when patients are admitted, discharged, or transferred between units
- Emergency department flow – monitoring patient arrival, triage completion, and discharge events
- ICU activity tracking – recognizing critical care events and staff response patterns
- Rehabilitation session monitoring – tracking therapy session start/end times and patient progress milestones
What makes this case stand out is the use of AI not for clinical diagnosis or treatment but to create digital situational awareness, turning physical OR activity into actionable data.
This is what automating clinical workflows is all about – using technologies like AI and ML to solve specific issues your healthcare organization faces.
AI-powered surgical scene recognition
Leveraging ML and computer vision to enhance operating room efficiency
Benefits of optimized clinical workflows
Improved patient care
- Faster diagnosis and treatment due to reduced delays and streamlined handoffs
- More personalized care, as clinicians have easier access to complete patient data
- Fewer errors and omissions with automated alerts and decision support
Time savings for staff
- Less time spent on administrative tasks (e.g., documentation, data entry)
- Faster communication between departments and teams
- More time available for direct patient interaction and clinical decision-making
Reduced errors and delays
- Automation and standardization minimize human error
- Real-time visibility into patient status and task progress helps prevent missed steps
- Alerts and reminders ensure timely actions (e.g., medication, follow-ups)
Operational efficiency and cost savings
- Better use of hospital resources (e.g., operating rooms, equipment, staff)
- Decreased readmissions and unnecessary tests due to clearer care pathways
- Lower overhead by eliminating redundant processes
Data-driven decision making
- Structured, accessible data enables better care coordination and strategic planning
- Easier performance tracking through real-time workflow metrics
- Supports continuous improvement through measurable insights
- Accelerates data analytics in clinical trials by improving recruitment and coordinating data more efficiently
Reduced staff burnout
- Lower cognitive and administrative burden
- More predictable, less chaotic workdays
- Higher job satisfaction
Scalability and adaptability
- Easier to integrate new technologies like AI, RPA, or telehealth
- Flexible workflows that adjust to changing care models, patient volumes, or regulations
- Readiness for future digital transformation initiatives
Conclusion
At the end of the day, better workflows mean better care. When hospitals can make systems work and give clinicians back their time, everyone benefits, including patients, providers, and staff alike.
Clinical workflow optimization isn't just a technical upgrade but a way to make healthcare work better for the people at the heart of it.
Ready to transform your healthcare operations? At Binariks, we specialize in developing AI-powered solutions that streamline clinical workflows, reduce administrative burden, and deliver measurable ROI. From OR scheduling optimization to EHR integration , our healthcare technology experts can help you reclaim lost time and resources while improving patient outcomes.
Contact us today to discuss how we can help you solve your healthcare organization's specific challenges.
Share

