The government mandated all healthcare providers to give patients more access to their personal health information as part of the 21st Century Cures Act. CMS Interoperability and Patient Access final rule encourages payers and providers to facilitate patient data sharing.
CMS patient access rule benefits all parties involved. Increased interoperability guarantees that providers can access an individual's care history to make educated clinical decisions, potentially leading to better patient outcomes. Moreover, access to personal health information may increase patient involvement in treatment decisions. Patients get more control over their treatment.
Binariks prepared for implementing CMS Interoperability Rule Compliance long before it came into force. Thus, we already have healthcare interoperability projects in our portfolio and can help with yours.
Here we share some essential things to know about CMS Interoperability Rule Compliance.
What does it mean for patients
The modern healthcare industry is patient-centric. Thus, giving people control over their medical records is essential to empowering patients. It contributes to MOH's efforts to create a value-based health care system that meets the needs of patients.
The ONC Cures Act's final rule defines and implements the Act's 21st-century compatibility requirements. The new rules have the following advantages for patients:
- Protection of confidentiality and safety
This rule enables patients to have secure access to their electronic medical data. Patients can use applications to retrieve their medical records using the same highly secure protocols already used in other industries, such as travel and banking applications.
- Expanding the possibilities (purchasing care services and cost management)
The goal is to increase access to data that provides insight into the quality and cost of care to improve patient choices in health care.
- Access to records
Patients can access their medical records through any app of their choice with API-based compatibility between their provider's electronic records and their smartphone or other apps.
What do healthcare providers need to know about interoperability rules
The ONC Cures Act Final Rule increases control over information by adopting an application programming interface (API).
APIs improve electronic healthcare data exchange by sharing health information with patients or exchanging data between a payer and a provider, or between two payers. The API enables a seamless exchange of information between software systems:
- Electronic medical records (EER),
- practice management systems,
- payer claims platforms,
- mobile patient applications.
APIs facilitate FHIR, a standard for the electronic transmission of health information. It allows doctors and organizations to standardize the presentation and exchange of patient health information, regardless of how local EER and other software systems display or store data.
CMS-regulated payers are required to accept APIs under two interoperability rules:
- Final (The Interoperability and Patient Access final rule)
- Proposed (CMS Interoperability and Prior Authorization Proposed Rule).
The CMS's Interoperability and Patient Access final rule puts patients first by providing them access to their health information when needed and in the best way possible.
CMS interoperability healthcare provisions
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services play a definitive role in healthcare and insurance programs. These organizations create regulations aimed at making medical data exchange more transparent.
Check the list of the latest CMS interoperability provisions below.
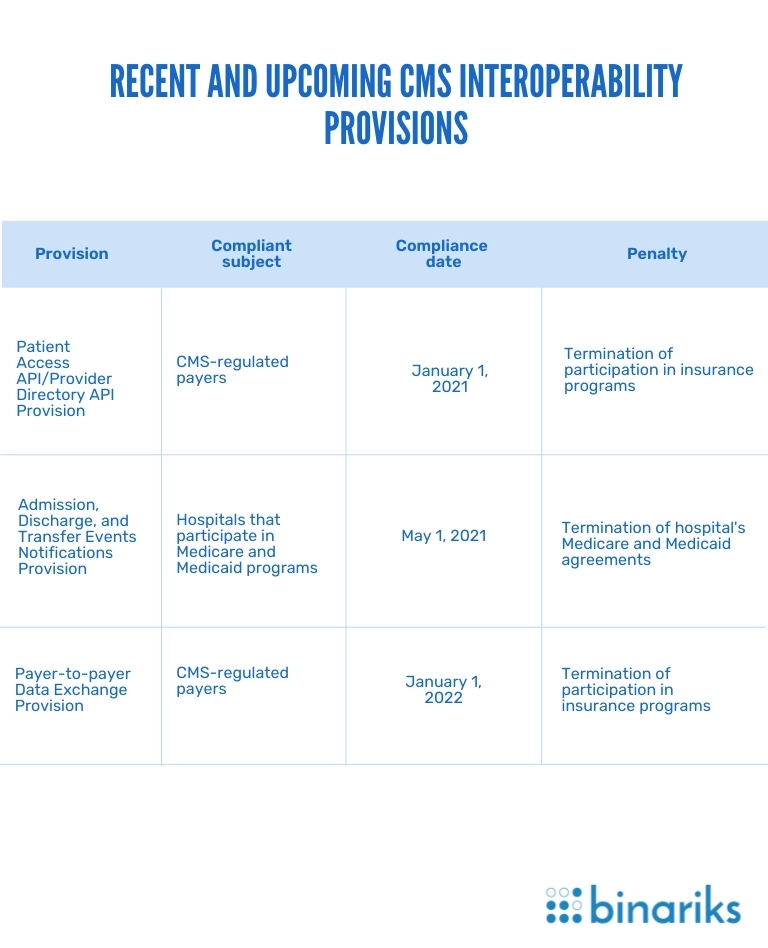
Patient Access API/Provider Directory API Provision
According to this CMS interoperability provision, there are two types of FHIR-based APIs that CMS-regulated payers must implement in their software.
- Patient Access API. Through this API, enrollees can request data on claims, costs, and clinical measures using CMS interoperability and patient access.
- Provider directory API. This API allows patients to access provider directories. The directories provide information on all entities participating in a particular health plan, namely hospitals, third-party administrators, pharmacies, practitioners, etc. It keeps the patients informed about the medical services they receive.
Admission, Discharge, and Transfer Events Notifications Provision
This CMS interoperability rule requires hospitals to send event notifications to practitioners and care managers when a patient is admitted to a hospital, transferred to another facility, or discharged home.
The ADT Provision determines a fixed format for such notifications necessary for software interoperability. The message has to include the patient's name, the treating provider's name, the sending institution's name, and, optionally, the patient's diagnosis.
Payer-to-Payer Data Exchange Provision
It requires CMS-regulated payers to exchange patient data with others upon an enrollee's request. The regulation helps patients easily coordinate their care and switch between health plans. There are no specific demands for EHR APIs applied during such health information exchanges.
ONC interoperability healthcare provisions
ONC is one of the most influential actors in digital healthcare. This organization has created numerous interoperability healthcare provisions that improve management efficiency. Go on reading to know the most valuable ones.
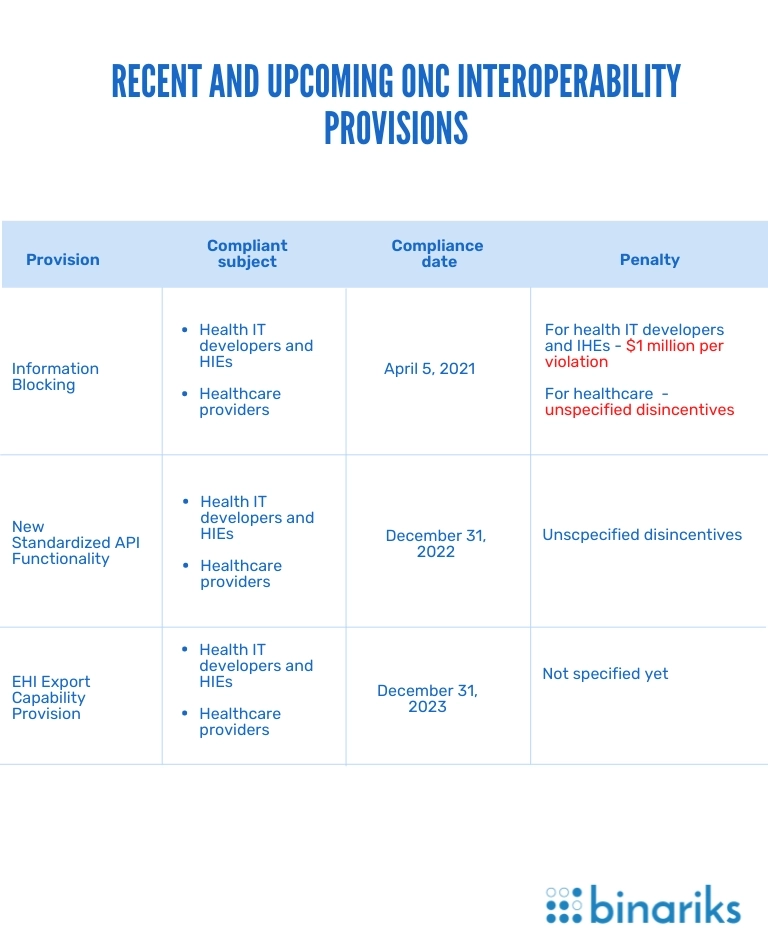
Information Blocking
According to this ONC interoperability rule, healthcare businesses must provide patients with data covered by the USCDI on request. The key requirements for health IT providers are building FHIR APIs and establishing a standard online format in which patients will receive data.
At the same time, healthcare providers individually review each case of EHI healthcare blocking. In particular conditions, healthcare providers may avoid fines after withdrawing or declining a patient's data request.
New Standardized API Functionality
This ONC interoperability provision requires hospitals to use two standardized types of FHIR API-enabled functionality.
- For single patients. Such APIs connect EHR systems with third-party apps to access a patient's medical data.
- For a group of people. APIs connect EHR systems with machine learning and Big Data analytics software to help hospitals deliver better care for groups of patients.
Through standardization of API requests, the provision eliminates medical information exchange inconsistencies, which are the most common interoperability challenges.
EHI Export Capability Provision
According to this medical regulation, EHR users must be able to create export files with all EHI of a single patient. The provision also specifies the format and the classification for data to export. After its enforcement, healthcare providers will have to classify specific data elements, frequently stored and managed outside the core EHR systems, such as EHI. This means providing patients access to the related administrative and billing data upon request.
Why comply with interoperability requirements?
Interoperability regulation enables coordinated and efficient data transmission between information systems. It allows healthcare providers access to medical records such as prescription lists, discharges, hospital admissions, lab test results, and healthcare plans without unnecessary obstacles. Interoperable patient data aids in ensuring that patients receive the proper medications and the best care possible.
Here are the practical benefits you get when following CMS and ONC interoperability rules:
Enhanced collaboration
Healthcare data interoperability and patient access help you deal with problems that stand-alone systems cannot solve. It improves information exchange and systems collaboration. You can use combinations of apps, tools, and databases to solve challenges. For example, smooth connectivity of remote monitoring systems and EHR databases optimizes critical patient management.
Improved efficiency
The interoperability of health information systems allows you to automate many processes. Therefore, healthcare teams spend less time on routine activities. Interoperability rules can also boost productivity by improving the capacity to share important information for patient matching. This saves clinical and administrative staff time by eliminating the need to manually ensure that a patient's data belongs to the right person.
Easier technology adoption
Interoperable systems in healthcare are adaptive to innovation. You enhance your system's connectivity using common data formats and standards for health information exchanges (HIEs).
Quality mark
Healthcare regulatory compliance can make you an ONC-certified company. As a result, you will receive a quality mark proving your status as a regulation-compliant company. It may become a decisive factor for potential clients.
Participation in programs
Regulatory compliance in healthcare is essential for companies that aim to participate in Medicare/Medicaid and CMS-initiated insurance programs. It also allows healthcare businesses to earn incentives from Quality Payment Programs. That encourages clinicians, eligible hospitals, and Critical Access Hospitals to adopt, implement, and upgrade to Certified Electronic Health Record Technology and to demonstrate meaningful use of CEHRT.
Improved publicity
Upon achieving medical regulatory compliance, numerous lists of ONC-certified and CMS-certified companies will mention your business. Also, it will appear in reputable industry press releases that make your organization more popular and allows you to expand its outreach.
Most importantly, software interoperability enables you to collect all patient data in one place. This allows the healthcare team and patients to access medical records whenever they need and improves healthcare services.
Want to reap these benefits? Get to know more about interoperability rules standards and provisions.
Basic Healthcare Interoperability Standards
The two main healthcare data migration standards regulate the nationwide exchange of medical information. These are HL7 FHIR and USCDI. Let's take a closer look at both.
HL7 FHIR
The full name of this data interoperability standard is the 4th version of Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources from HL7 International. It specifies the format for HTTP-based RESTful APIs that ensure healthcare interoperability. One of the basic FHIR standards requires medical businesses to use three basic data formats: XML, JSON, RDF.
This medical regulation ensures EHR interoperability and seamless exchange of other medical data types.
USCDI
The US Core Data for Interoperability (USCDI) defines what pieces of information your healthcare company might share at a patient's request. This EHR interoperability standard covers basic classes of medical information. Meanwhile, these data standards in healthcare are rather general and leave many aspects of interoperability unspecified.
The main goal of HL7 FHIR and the USCDI is to promote consumer healthcare through efficient FHIR APIs and improved transparency.
What are the problems with implementing health data standards
Even though FHIR is a simple standard, changes in implementation create compatibility issues. Each FHIR resource has 10 to 50 attributes (e.g., demographic information about patients or pharmacy order info). However, providers select only some resource attributes. They don't make all of them required. As a result, data sharing is not implemented in a uniform way across the healthcare system.
Thus, to meet with the CMS patient access rule, you must agree on the necessary attributes of the resource, so your healthcare provider can build a better means of communicating information.
How to build interoperability that brings healthcare regulatory compliance?
Building a compliant interoperable system requires thorough preparation and a comprehensive development approach. Here are some general steps to meet regulatory requirements in healthcare interoperability correctly.
- Determine how healthcare interoperability standards and provisions apply to you—research all EHR interoperability and data standards in healthcare. Ensure to determine those that fit you and understand how to meet them for regulatory compliance in healthcare.
- Review your existing systems. Focus on improving your existing infrastructure instead of replacing it altogether. Review your systems for features that do not comply with interoperability regulations. Determine possible ways to fix such EHR interoperability issues.
- Build your interoperability strategy. Use the insights from your research to build a clear roadmap to regulatory compliance in healthcare.
- Align interoperability plans with the required functionalities. Do not forget about your business goals. Your infrastructure must both fit regulatory requirements in healthcare and improve organizational efficiency.
- Publish the required APIs. Comply with a recent CMS interoperability provision: implement a patient-access EHR API and a provider-directory EHR API.
- Enable payer-to-payer data exchange. Be ready to exchange patient clinical data with other CMS payers at an enrollee's request.
- Master and implement the HL7 FHIR standard . Learn the essentials of FHIR API management. Implement the basic components of the CMS Interoperability solution, such as an API Gateway, an orchestration hub, and a privacy engine.
- Structure data according to standard terminologies. Make sure you use the FHIR standard vocabularies for different types of information.
- Enable top-notch security practices for sensitive data. Label data sets covered by security-centered healthcare IT regulations, such as HIPAA. Protect them with top-notch access management practices, security safeguards, and threat management tools.
- Train your staff to comply. Educate your staff to handle requests and manage health information exchanges (HIEs) according to regulatory requirements in healthcare.
- Establish a consent management process. Patient consent is essential for any actions with their data. Ensure to implement features allowing you to collect and track consent for all EHR APIs within your system.
- Implement auditing and testing tools for your software. Ensure continuous auditing and regularly review your systems for compliance with CMS and ONC interoperability rules.
Best Solution for Meeting Healthcare Interoperability Standards and Provisions
Even if you clearly understand all the rules and have a roadmap for building regulation-compliant interoperability in healthcare, you may still face insurmountable interoperability challenges. The most common is the lack of technology expertise, essential for building connectivity and APIs that suit the FHIR standard.
When outsourcing becomes a solution, a dependable technology partner with solid experience delivering regulatory-compliant medical software will help you solve the most painful interoperability challenges. We will help you increase ROI for EHR and yield long-lasting benefits.
Binariks is here to help you implement your plans. We handle all stages of the software development lifecycle to deliver highly scalable solutions. Our dedicated, experienced developers build efficient FHIR healthcare APIs that fit the basic health data standards. Learn more about our expertise in our portfolio .
Contact us to discuss your needs. It is just about time to boost your business with state-of-the-art systems that comply with the primary healthcare interoperability standards.
FAQ
Share

