Enterprise RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is the implementation of RAG systems at a production level within large organizations.
At the business level, you're investing in enterprise RAG to unlock your organization's knowledge and drive measurable returns. You expect faster support responses, smarter decision-making, and reduced operational overhead. Instead, you may face hallucinations, irrelevant answers, and skeptical stakeholders questioning the entire initiative.
In this article, we break down exactly why RAG fails, reveal the specific RAG pitfalls, killing accuracy and business value, and show you how to build an enterprise RAG system that actually delivers ROI – with real-world examples and a practical implementation roadmap.
So, why does RAG fail?
Why so many enterprise RAG projects fail
Enterprise RAG fails more often than it succeeds because it's usually deployed without a clear understanding of enterprise data complexity or clear metrics of success. The failure rate is actually quite astonishing: only 30% of enterprise RAG pilots reach production, and among those that do, only ~10–20% show a measurable ROI.
Every company with resources wants RAG, as it is treated as a cutting-edge must-have in enterprise AI. However, given how complex RAG Implementation is, what often happens is skipping the Why and jumping straight to the How.
Enterprises often find themselves unable to work around RAG pitfalls. One common scenario is companies aimlessly scanning all of their documents, hoping to get some insight from AI, without understanding the scope of the actual ROI target.
Other problems with RAG are:
It does not matter whether your company is large, because having resources to pull into RAG is not an indicator of success. Its clear goals, sound strategy, and its implementation that really matter. Enterprise RAG should not be treated like just another chatbot where only Generative AI development matters. It really needs UX, observability, governance, and business integration.
Common RAG pitfalls killing accuracy & ROI
Here is the list of most of the common enterprise RAG failures, with a detailed look into each enterprise RAG challenge:
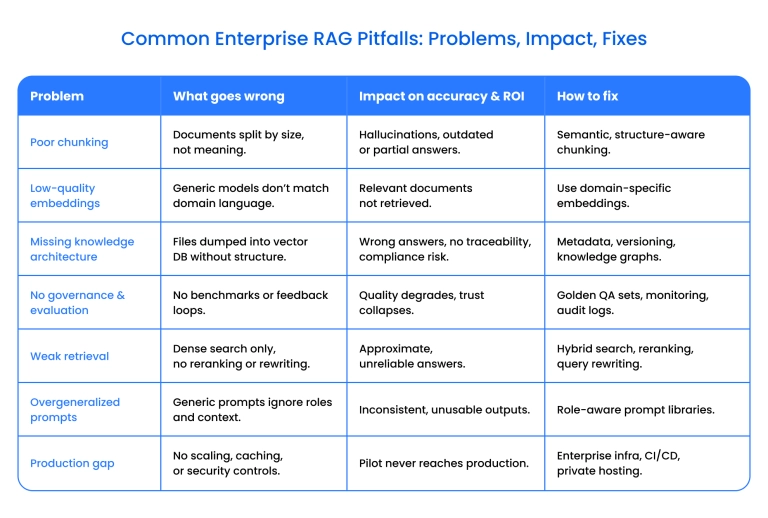
Poor document chunking and indexing
RAG depends on document chunks that are context-rich and retrievable. The mistake occurs when chunking is inaccurate, with chunks being either too large or too small. There is also a term called naive chunking, which means that concepts are chunked mid-thought, or they fail to capture usable units.
Model hallucinations are also a part of this mistake. The risk of poor document chunking for enterprises is that outdated or misaligned document versions appear in answers.
The ways to address these issues include:
- Semantic chunking based on structure, not size
- Using table/section-aware parsing
- Adding chunk scoring before injection
Irrelevant or low-quality embeddings
In the context of RAG systems, an embedding is a method for converting text into a list of numbers (a vector) that captures its meaning and semantics. If the embedded models are mismatched to your domain, retrieval will fail even if the content is of high quality.
For example, off-the-shelf models (e.g., those trained on Wikipedia) are not suitable for specialized fields such as finance, medicine, or law. Without normalization, inaccurate similarity scoring is a likely outcome.
The solution is to use domain-specific embeddings (e.g., e5-large-v2) and to run regular retrieval evaluations with Precision@k and MRR.
Wrong or missing knowledge architecture
Dumping all your files into a vector DB does not constitute an actual knowledge base. This is because without a semantic map of your content, RAG cannot retrieve the proper context.
Without the right knowledge architecture, you would not have classification of docs by use case, source, or audience. It also means no version control, making old and new policies mix. Finally, a lack of access-control metadata results in the wrong users seeing the wrong information.
All of this results in an inability to trace the origin of the answer. As a result, there is a real risk of sensitive data leaking and the audit trail failing.
The solution is using knowledge graphs, tagging, versioning, and document-level visibility flags.
Lack of governance, evaluation, and monitoring
Enterprise RAG implementation requires human evaluation and feedback loops to function with accurate answers and without hallucinations.
This includes:
- QA benchmark for regression detection
- Source attribution
- User feedback loop
- Audit logs
Building a "golden" QA set of curated question–answer pairs, reviewed by subject matter experts, that can later be used for regression testing, is a significant part of what constitutes a successful evaluation. Overall benchmark accuracy should be set at approximately 85-90 per cent.
Weak retrieval
Retrieval is the backbone of RAG, and it is where enterprise RAG most often fails. If it fails, critically important answers become unreliable, and high-value users will abandon the system.
- Top-k dense search alone is insufficient, as it yields approximate matches rather than precise ones.
- You will not get exact matches without hybrid search, which is the only method that combines dense semantic search with sparse keyword-based search.
- The retrieved chunks must be reranked to determine which ones are most useful in the current context. Without reranking, low-quality chunks will take up too much space in the context window.
- Users often ask vague or poorly structured questions (e.g., "What's our policy on leave?"). Without a query rewriting layer that expands or clarifies user intent (e.g., "Return latest HR leave policies for full-time employees"), the retriever might not surface the right documents.
Overgeneralized prompts
One-size-fits-all prompts copied from ChatGPT demos are not suitable for specific enterprise RAGs, as they are simply too generic and lack any real nuance. You should not be fighting the system for a usable answer. Moreover, effective prompts should not compromise the system's ability to recognize the user's role within organizations.
To fix all of it:
- Build prompt libraries with SMEs
- Test across roles, domains, and edge cases
- Include output format conditioning.
The Production gap
Many RAG proofs-of-concept fail in production because teams underestimate real infrastructure and operational requirements.
For example:
- Without caching, the cost per query grows quickly and becomes unsustainable at scale.
- Without defined latency SLAs, users experience slow responses and inconsistent RAG behavior.
- Without secure or private hosting, the system is blocked by information security and never reaches production.
- Without CI/CD pipelines for prompt and model updates, every change can become an error.
If you do not want to grow out of pilots, you have to treat RAG as an enterprise product. Add monitoring, canary testing, autoscaling, retry logic, and DevOps pipelines, and use VPC/private hosting.
From strategy to production: expert guidance for every AI implementation step.
Compliance & security issues that break RAG in enterprises
A quick RAG prototype may work in a hackathon or internal demo, but when it comes to deploying RAG at enterprise scale, compliance and security are key. Most "scrappy" RAG implementations break down completely when exposed to real-world enterprise constraints because:
- They may ignore access controls and permissions
- They have no audit logs or traceability
- They are embedding sensitive data without redaction, which ends up risking leaking PII
- They use open models such as GPT or Anthropic without guardrails
- They index old documents without a proper policy for data freshness
Enterprise RAG deployment that has compliance and security in mind is supposed to work by privacy-by-design principles. Under data minimization, you make sure that only the necessary data is being indexed.
Personal information has to be purged from all system components upon request, and there should be extraction capabilities for user-specific information. Even if not purged, there should be mechanisms to guarantee privacy, such as federated learning, differential privacy in embeddings, and proper encryption.
Other compliance and security components are:
- Structured logging
- Real-time monitoring of anomalies like suspicious activities and attempts to log in
- Retention periods for all data
What a high-performing, enterprise-ready RAG system looks like
A successful RAG system isn't just an LLM with a retriever slapped on top. In the enterprise, RAG is a full-stack architecture that is scalable, secure, and deeply integrated into business workflows. To deliver real ROI, it needs more than "question → search → answer."
Here are all the components that should be a part of it.
Structured knowledge architecture
At the core of good RAG is a clear map of your internal knowledge. In simple terms, the system should know what it knows, where it came from, and who should see it. That includes:
- Clean, classified document sources
- Metadata-driven filtering (e.g., version, author, department)
- Hierarchical data segmentation (e.g., customer docs ≠ internal wikis)
Smart chunking & domain-aware embedding
Chunking has always to preserve context, and embeddings must be tuned to your domain. Retrieval is only as effective as the signals you provide. The components include:
- Adaptive chunking strategies based on document structure, not token limits
- Domain-specific embedding models
- Embedding hygiene: deduplication, redaction, and filtering
Hybrid retrieval with reranking
Enterprise RAG deployment should combine several types of retrieval (plus reranking):
- Dense (vector) search for semantic matches
- Sparse (keyword) search for precision
- Cross-encoders or LLM reranking for top-k results
Enterprise-grade access control & compliance
A real enterprise system respects:
- RBAC (Role-Based Access Control)
- Document-level permissions
- GDPR / HIPAA / SOC 2 / internal infosec rules
Feedback loops, evaluation, and monitoring
Accuracy and trust are measured with:
- Groundedness metrics (e.g., faithfulness, answer support scores)
- Human-in-the-loop feedback
- Analytics dashboards
Integration into real workflows
High-performing RAG is integrated into various parts of the workflow and is not a standalone product. They show up:
- In CRM tools as context-aware assistants
- In support portals
- In internal search, replacing static knowledge bases
Measuring RAG quality
Here is a short overview of every factor that measures the quality of RAG:
- Groundedness (Faithfulness)
Does the answer actually reflect the retrieved content?
Even if a response looks plausible, it must be traceable to the sources.
- Answer Relevance
Is the answer relevant to the user's question?
This checks how well the retrieved documents and generated output match the user's intent.
- Retrieval Accuracy (Recall & Precision)
Did the retriever find the correct documents?
- Recall: Were all relevant documents among the top-k retrieved?
- Precision: How many of the top-k were actually relevant?
- Hit@k: How often the correct chunk appears in top-k results
- Compliance & Safety Evaluation
Does the system return secure, compliant, and appropriate content?
The content should not contain confidential information and should be free of access control violations.
- Source Attribution and Traceability
Can users verify the answer?
If the user can't see why the system answered, they won't trust it even if it's right. A trustworthy RAG provides:
- Source links or doc IDs
- Highlighted supporting text
- Confidence levels or citations
- Business Impact Metrics
Is RAG actually helping the business?
Look beyond text quality and into ROI, which can look like:
- Time saved per user
- Fewer support tickets
- Faster onboarding or sales enablement
- Increased knowledge reuse, etc.
Gain a competitive edge with our comprehensive AI guide
Get the knowledge you need to lead with Generative AI

How to build an enterprise RAG that actually delivers ROI
Below is a practical roadmap for building an enterprise RAG pipeline that meets the needs of the enterprise and sustains long-term value.
1. Knowledge audit
Start with identifying what your organization "knows" and where that knowledge lives. The key is that high-impact trusted data should be a priority. To do it:
- Map data sources: documents, wikis, databases, CRM notes, policies, etc.
- Classify content by type, sensitivity, business unit, freshness, and usage.
- Define what should be retrievable and what must be excluded.
2. Define domain ontology / Semantic layer
Next, build a semantic model of your enterprise's language and structure. The goal is to make your RAG "understand" how your business speaks and thinks. In particular:
- Define key entities (e.g., products, regions, roles).
- Identify synonyms, acronyms, and internal lingo.
- Tag documents with domain metadata (departments, purpose, topics).
3. Document preparation
Prepare documents for ingestion by the enterprise RAG. The retriever should receive only high-quality data that will end up being useful.
- Clean: remove duplicates, outdated versions, and irrelevant pages.
- Chunk: break into coherent units using section titles, tables, etc.
- Annotate: add metadata for source, version, access level, and topics.
4. Choose optimized embedding & reranking models
Use domain-relevant models:
- Embeddings: prefer fine-tuned or task-specific over generic ones.
- Rerankers: Utilise bi-encoder and cross-encoder stacks for more intelligent top-k selection.
- Test models using your actual corpus and queries.
Here are some of the model examples:
Embedding models:
- bge-base-en-v1.5 (BAAI) – strong general-purpose performance
- text-embedding-3-small (OpenAI) – high quality, multilingual support
Reranking models:
- cross-encoder/ms-marco-MiniLM-L-12-v2 – fast and accurate
- bge-reranker-large (BAAI) – excellent top-k reranker for English corpora
5. Build a hybrid retrieval pipeline
To retrieve the right content under real-world query conditions, you should combine dense and sparse retrieval, where dense stands for semantic search, and sparse means keyword-based exact matches.
Other components to add to the pipeline are:
- Reranking
- Document scoring
- Retrieval confidence thresholds
- Fallback logic ("I don't know" when uncertain).
6. Add RAG guardrails
RAG guardrails are what make the answers reliable. Best practices are:
- Prevent hallucinations with the help of retrieval thresholds and citation linking.
- Apply role-based access controls and data visibility filters to ensure secure access and visibility.
- Configure safe fallback behaviors for low-confidence outputs. If retrieval fails or the score is too low, return a "no answer" response instead of letting the LLM guess. You can suggest follow-up clarifications to rephrase the text.
7. Implement the evaluation framework
You must establish a feedback loop to facilitate continuous improvement. To do so, you need to define structured evaluation metrics:
- Groundedness: is the answer traceable to sources?
- Retrieval quality: recall, MRR, nDCG
- Answer relevance: clarity and usefulness
- Feedback loops: CTR, thumbs up/down, time saved
8. Private hosting: On-prem, VPC, confidential compute
Deploy in a way that meets information security and compliance requirements.
- Use VPC or on-prem infrastructure for vector DB and LLMs
- Enable audit logs and monitoring.
- Support private GPT-style endpoints (e.g., Azure OpenAI, Mistral on AWS)
9. Business integration: Workflows, APIs, interfaces
RAG must live where people work. This means it should be included in day-to-day work. To support this:
- Integrate with CRMs, helpdesks, dashboards, and chatbots.
- Use APIs to plug into legacy or custom tools.
- Build high-quality UI components with feedback and the option for support interaction.
10. Continuous improvement
RAG is not a one-time launch; it should evolve in tandem with your business, balancing user needs and business goals. To support this:
- Reindex when content updates.
- Retrain or RAG or fine-tuning models based on feedback and drift.
- Adjust thresholds and document scoring strategies.
- Review business KPIs regularly (e.g., deflected tickets, time saved).
Examples of RAG delivering ROI
Here are two practical examples of enterprise RAG adoption that actually delivered on ROI. We describe this to illustrate realistic business logic.
First, let's look at an example of an internal engineering assistant. Imagine a global software company that deployed a RAG system to help developers and DevOps teams quickly access internal knowledge.
What it actually did:
- Let developers ask questions like, "Where's the Terraform module for staging?" or "How do I roll back a service in production?"
- Pulled answers from GitHub reports and CI/CD logs, and not just Confluence
- Integrated with Slack
- Applied team-level access so infra engineers didn't see frontend stuff, and vice versa
ROI RAG:
- Cut DevOps support tickets by 32%
- Reduced onboarding time for new engineers by ~40%
- Saved dev leads 4–6 hours/week searching across Confluence and GitHub
A second example is that of a B2B SaaS company that added RAG to its Zendesk workflow to assist human agents in real-time.
What it did:
- Surfaced exact API snippets or setup steps when customers asked things like "Why is OAuth failing on v2.1?"
- Pulled answers from changelogs and internal service logs
- Let agents rate the relevance of answers, improving suggestions over time
- Proactively suggested similar resolved tickets to avoid duplicate effort
ROI RAG:
- 27% faster first response time
- 18% lower ticket resolution time
- Tier 1 agents resolved 40% more tickets without escalation.
Conclusion
You've seen the RAG pitfalls that sink most enterprise RAG projects. The question now isn't whether enterprise RAG can deliver ROI – it's whether you have the right partner to make it happen.
Enterprise RAG implementation is complex. Between chunking strategies, hybrid retrieval, access controls, and evaluation frameworks, there are dozens of decisions where the wrong choice kills accuracy or creates security violations. You need experts who've navigated these challenges before, not consultants learning on your budget.
At Binariks, we've engineered enterprise RAG systems for healthcare, financial services, and insurance – sectors where hallucinations aren't just embarrassing, they're liability. We understand what separates successful enterprise RAG deployment from expensive experiments.
How we help:
- End-to-end AI and ML development
- Data architecture consulting
- Secure deployment support
- Fine-tuning and embedding strategies
- Evaluation frameworks
- Multi-system integrations
You have the knowledge and the business case. What you need is a team that's solved enterprise RAG implementation challenges before and can help you avoid the pitfalls that derail 70% of projects.
Ready to build enterprise RAG that actually delivers ROI?
Share

