Healthcare data is constantly growing at an exponential rate. This growth is driven by several factors, including advancements in medical technology, increased use of electronic health records (EHRs), the growing use of wearable devices, and the widespread adoption of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring.
There comes a point where traditional cloud computing cannot sustain this level of growth due to latency and bandwidth limitations. Edge computing in healthcare is capable of handling vast amounts of healthcare data, as it is perfect for handling real-time data processing in healthcare. In this article, we discuss how edge computing improves healthcare today.
The bottlenecks of traditional cloud-based processing
Traditional cloud-based processing and cloud healthcare solutions experience several bottlenecks, which can be solved by edge computing in healthcare. Here are some of the most common of these bottlenecks:
- Latency and bandwidth limitations: Data transmission between end-users and cloud servers can introduce significant delays, especially for healthcare applications requiring real-time data processing. Moreover, bandwidth limitations lead to slower data transfer. Delays in real-time data processing can lead to serious repercussions in healthcare applications.
- Data privacy and security concerns: Centralized systems are more susceptible to cyberattacks, to which cloud computing can serve as a solution. Storing sensitive data on third-party servers requires high trust in the cloud service provider's security measures.
- Scalability: The high volume of healthcare data is difficult for traditional infrastructure to comprehend. Dynamically allocating resources to meet varying demands can be complex, leading to either over-provisioning (wasting resources) or under-provisioning (performance degradation). Distributing workloads across multiple servers to prevent any single server from becoming a bottleneck requires sophisticated management.
- Cost management: Sending data to central storage and transferring it in and out of the cloud can be costly. Edge computing in healthcare can be significantly cheaper than that.
- Connectivity issues: Unreliable internet access can be an issue in remote and rural areas. Edge computing mitigates these connectivity issues by processing data locally at or near the data source.
How edge computing revolutionizes healthcare data processing
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that brings processing and data storage closer to the data sources. This approach minimizes the distance data must travel and reduces latency and bandwidth use. The main principle is to process data near the data source (at the "edge" of the network) rather than relying on a centralized cloud server.
Edge computing for healthcare offers a fantastic solution for dealing with vast amounts of data, such as EHR, patient data, information from remote monitoring devices, medical imaging, and financial information. This makes it one of the hottest data engineering trends to exist today.
All of the benefits of edge computing in healthcare stem from the fact that it decentralizes how data is processed. Smaller clusters of information centers are more efficient than having one centralized system for storing patient and hospital data, including remote patient monitoring. Here is the comprehensive list of benefits of edge computing in healthcare:
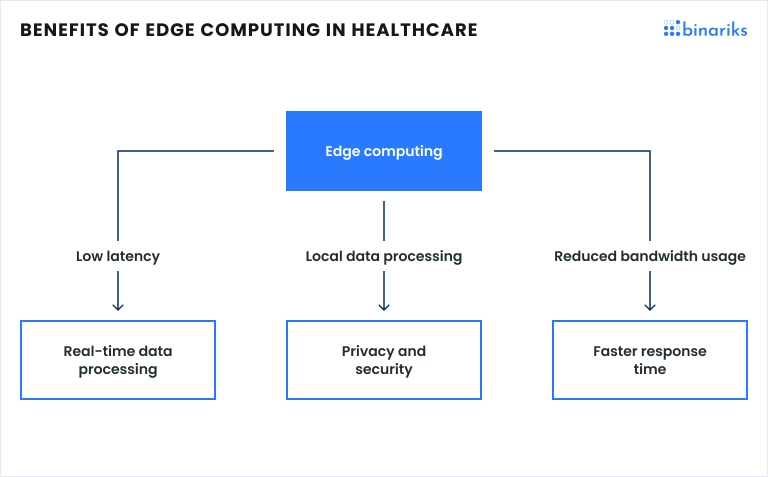
Reduced latency
Edge computing enables real-time data analysis of medical devices (such as patient monitors, wearables, and imaging equipment) and fast access to critical information due to low latency.
This immediate processing is crucial for time-sensitive applications like remote patient monitoring and emergency response to medical crises. The speed and efficiency of data processing are greatly improved with edge computing because data no longer has to travel long distances.
Enhanced scalability
Edge computing provides a scalable infrastructure that can grow with the healthcare facility's needs. By adding more edge devices, healthcare providers can handle increasing amounts of data without overloading a central server. This gives healthcare organizations flexibility, which is vital as the industry constantly presents shifting demands. Even more important is the ability to grow with healthcare edge computing, which is relatively fast and smooth.
Edge computing in healthcare seamlessly integrates into existing infrastructure. It also allows for load balancing as single devices or servers have less chance of becoming a bottleneck.
Moreover, edge computing for healthcare is comfortably deployable in very different settings, from large hospitals to the smallest clinics. Healthcare edge computing even enhances remote patient monitoring, which reduces hospital visits.
Streamlined workflows
Edge computing for healthcare helps streamline workflows in various ways. First, edge computing facilitates the integration of different medical devices and systems, allowing them to communicate and share data seamlessly. This integration reduces the need for manual data entry and ensures that patient data is consistently updated across all systems.
Edge computing in healthcare systems also automates data collection and preliminary analysis tasks. For instance, edge devices can automatically process data from patient monitors and alert staff only when intervention is needed. As a result, healthcare workers can dedicate their time to other tasks.
Optimized resource utilization
Edge computing ensures computational resources are utilized more efficiently by processing data locally. This reduces the load on centralized servers and optimizes the performance of medical applications.
Allocating resources with edge computing in healthcare systems is cheaper than more traditional clouds. Resource allocation can be further improved with AI algorithms.
Improved security and privacy
Security breaches can cause substantial financial and reputational loss for healthcare companies, making them one of the biggest current challenges of big data in healthcare .
By processing data locally, healthcare edge computing reduces the amount of sensitive patient information transmitted over networks, minimizing the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations such as HIPAA.
Keeping data close to its source is a very secure way of handling data, as it can be protected even before it is sent to the data source. Moreover, healthcare facilities can maintain tighter control over patient data so that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
Healthcare organizations can use edge computing for healthcare data privacy by scaling up and personalizing privacy solutions.
Edge computing in the healthcare market decreases the possibility of data breaches. However, if data is indeed breached, it is easier to prevent continuous access to this data from a single access point.
Better patient care and patient experience
Edge computing in healthcare helps to interpret patient data from wearables better. It enables predictive analytics, which is capable of finding trends and patterns crucial for the identification of diseases and treatment planning, as well as big data applications of healthcare .
Moreover, it also helps improve constant remote patient monitoring. Both patients and healthcare professionals gain immediate access to essential healthcare data. Medical errors are far less likely to happen with this approach. Edge computing also potentially means faster and more accurate diagnoses and personalized care.
Real-world applications of edge computing in healthcare
Remote patient monitoring
One of healthcare's most common and crucial edge computing applications is remote patient monitoring. It is most commonly used for chronic, non-communicable diseases, such as diabetes and cardiac diseases, which require chronic care management to let patients live longer with improved quality of life and fully manage the diagnosis.
Remote patient monitoring with healthcare edge computing is also crucial when patients cannot regularly access their care team because they live in remote and rural areas. This is also true for immobile and elderly patients.
With remote monitoring devices, patients can have better access to healthcare as the system sends regular updates to the care team on the status of the condition or events like falling. This allows the care team to react promptly to all changes, ensuring immediate and effective management of treatment.
Remote monitoring and real-time data processing in healthcare are safer with edge computing as it is better at handling sensitive data than a centralized cloud.
The low latency also means faster interactions between the patient and the care team, further enhancing the system's efficiency.
Some of the examples of remote patient monitoring done with edge computing are:
- VivaLNK wearable remote monitoring devices
- Philips Healthcare remote monitoring devices
- Medtronic cardiac monitoring devices and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems
- Intel & Flex remote monitoring management program
- Diabetacare diabetes management system
Telemedicine and telehealth services
During telemedicine consultations, edge computing can process and analyze patient data locally. This leads to more accurate remote diagnoses because all necessary data is available instantly. For example, Intel & GE Care Innovations Health Harmony uses edge computing to process data.
Telemedicine also involves emergency consultations where the lives of patients can be at stake, such as heart attacks, strokes, or severe trauma. The real-time, low latency provided by edge computing for healthcare can save lives. For example, The Mayo Clinic has a tele-stroke program where neurologists provide immediate consultation to local ER doctors, helping them quickly diagnose and treat stroke patients (Source ).
Patients do not have to be in an emergency to enjoy the benefits of edge computing in healthcare. It is also simply convenient to receive a consultation from the comfort of your home without interruption.
Remote surgical assistance
One of the impressive edge computing applications in healthcare is remote surgical assistance, also known as telesurgery. The doctors are now capable of operating remotely using high-definition video broadcasts and robots. 5G networks are used to ensure no time delays between the operating room and the doctor leading the surgery from anywhere in the world.
In 2019, Chinese doctors conducted the first successful remote brain surgery using 5G technology. The surgeon, located miles away, controlled robotic instruments to perform the procedure on a patient with Parkinson's disease (Source ).
In another example, Proximie's Global Impact is a platform that uses augmented reality (AR) and edge computing to allow surgeons from different locations around the world to collaborate in real time.
This includes remote areas where local surgeons perform surgeries under the guidance of specialists who provide real-time instructions and visual aids via AR. The first surgeries under this program were performed in Kenya in 2020. Since then, the initiative has expanded to Ethiopia and the Dominican Republic (Source ).
Emergency response and ambulance services
Ambulances equipped with edge computing devices can process patient data on the way to the hospital. Paramedics are able to communicate real-time information directly to the receiving hospital, bridging the knowledge gap between paramedics and the hospital before and after the handover.
They can livestream patient vitals to the hospital and promptly access patient data, enabling them to gather information about the patient's medical history and complex treatment protocols.
Medical imaging
Medical imaging equipment, such as MRI and CT scanners, can leverage edge computing for medical applications to process images locally. This reduces the time required to analyze scans and provides faster results.
Traditional centralized processing might take hours due to data transmission and queuing delays. With healthcare edge computing, this time is reduced to minutes or even seconds, enabling quicker diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Edge computing enables the deployment of AI algorithms directly on imaging devices. These algorithms can identify anomalies in real time.
Siemens Healthineers' SOMATOM Force CT scanner can perform scans with a rotation time as short as 0.25 seconds. This rapid data acquisition, combined with local processing, significantly reduces the total scan and analysis time. For example, a full-body scan that might take several minutes traditionally can now be completed and processed in seconds to minutes.
Other potential edge computing use cases in healthcare are:
- AI-assisted diagnostics
- Smart hospitals
- Personalized medicine
- Clinical trials and research
- Maintenance of medical equipment
- Drug inventory management
- Disaster relief
How Binariks can help with edge computing
Despite all the benefits, transferring from cloud-based processing to edge computing poses many challenges. Edge computing and healthcare data integration require professional expertise not always available in-house in healthcare companies, especially in smaller clinics. Some of the challenges of edge computing in healthcare providers face include:
- Lack of appropriate infrastructure that is crucial for scaling up
- Inadequate data governance policies for data security
- Lack of technical expertise
At Binariks, we have extensive experience implementing edge computing in healthcare organizations of various sizes. Here is what we can do:
- Designing and building edge infrastructure
- Seamless integration with existing systems
- Custom application development
- Optimization of AI and ML models
- Establishing security protocols
- Selecting edge management platforms
- Strategic consulting, training, and support
- Big data and analytics services
Conclusion
Edge computing for medical applications is a game-changer for multiple aspects of the healthcare sector, from diagnostics and emergency treatment to hospital management.
Real-time data processing, reduced latency, and optimized bandwidth are the necessary advantages today as the amount of healthcare data is growing exponentially, and the traditional cloud is no longer optimal for handling it.
Switching to edge computing today is a step forward for any healthcare organization, and Binariks is ready to help you with this vital transformation.
Share

