AI document processing is the use of artificial intelligence to automatically capture, interpret, validate, and route data from structured and unstructured documents within business workflows.
Instead of relying on static OCR templates or manual review, it treats document handling as a defined, scalable operational process integrated into core enterprise systems, where documents become a continuous data source rather than a manual bottleneck.
This approach is enabled by AI document automation, which applies machine learning, natural language processing, and rule-based validation to improve accuracy, reduce manual effort, and maintain control over data quality.
The implementation patterns discussed in this guide reflect how organizations apply these technologies in production environments, including enterprise-grade AI/ML development practices used to build secure, scalable document workflows across regulated and data-intensive industries.
After reading this guide, you will understand:
- How AI-based document processing differs architecturally from traditional OCR-driven workflows
- Which core components enable accurate extraction, validation, and downstream integration
- Where document processing delivers the highest operational impact across industries
- What capabilities matter most when evaluating AI-driven document workflows
- Which challenges typically surface during implementation and how teams address them
If you want a clear, implementation-focused view of how AI-powered document processing works in real systems, continue reading as the next sections break the concept down step by step, from fundamentals to production-ready use cases.
What is AI-powered document processing
AI-powered document processing refers to software systems that use machine learning and natural language processing to automatically extract, interpret, validate, and structure information from documents at scale. Unlike basic OCR, these systems understand document context, recognize semantic relationships between data fields, and adapt to new document formats without manual reconfiguration.
In practice, AI document processing solutions combine models for text recognition, layout analysis, entity extraction, and confidence scoring into a single processing pipeline. This allows documents such as invoices, contracts, forms, and reports to be converted into structured, system-ready data with predictable accuracy and traceability.
From an operational standpoint, AI-powered document processing is also tightly connected to AI for process documentation, where document flows are treated as part of broader business processes rather than isolated automation tasks. This makes document handling measurable, auditable, and easier to integrate into downstream systems such as ERP, CRM, or data warehouses.
A practical reference point for this approach is an AI-based document processing solution designed to operate within real enterprise workflows rather than as a standalone tool.
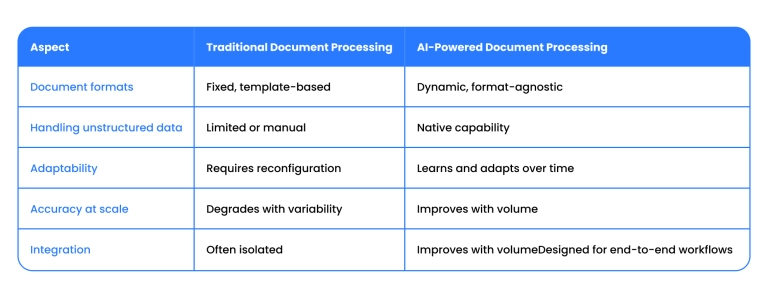
AI vs. traditional document processing
- Traditional document processing relies on fixed templates, manual rules, and deterministic logic to extract data from documents. This approach works only when document formats are stable and predictable, but it quickly breaks down when layouts vary, data is unstructured, or documents evolve over time.
- AI for document processing uses machine learning models that learn from data rather than predefined rules. These systems can interpret context, handle format variations, and improve accuracy as they process more documents, making them suitable for dynamic, real-world workflows.
The practical difference becomes especially clear when implementing document processing with AI as part of a broader digital product or platform.
AI-based pipelines are designed to integrate with downstream systems, support continuous updates, and scale alongside business growth, which aligns closely with modern software product development practices rather than one-off automation scripts.
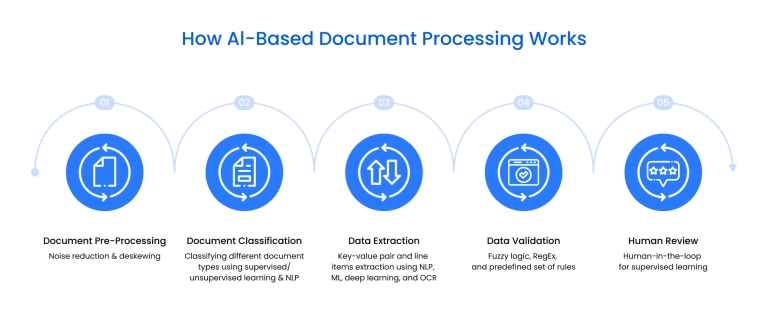
How does AI-based document processing work?
AI-powered document processing follows a controlled pipeline that converts raw files into validated, system-ready data. Each stage reduces variability, manages errors, and ensures extracted information can move safely into operational workflows.
Uploading and pre-processing
Documents enter through uploads, scans, or email ingestion. The system normalizes inputs by checking formats, correcting orientation, reducing noise, and enhancing image quality so downstream models operate on consistent data.
Document classification and data extraction
After pre-processing, AI-based document processing identifies document types using layout, structure, and semantic cues. Extraction models then apply OCR and language understanding to capture relevant fields from both structured elements and free text, depending on the document category.
Data validation and error handling
Extracted values are assessed against confidence thresholds, business rules, and reference data. Exceptions are flagged for review or corrected automatically based on learned patterns, containing errors before data reaches core systems.
Integration and output
Validated outputs are pushed into ERP, CRM, or analytics platforms, enabling document process automation across end-to-end workflows. This approach aligns with modern software product development , where document pipelines are built as scalable, maintainable components rather than one-off automations.
Post-processing and continuous improvement
Human feedback and system metrics close the loop. Corrections retrain models, accuracy improves over time, and data is normalized to internal standards to keep document-driven processes consistent at scale.
In practice, this approach turns document handling into a structured, repeatable system rather than a manual task. By combining automation, validation, and continuous learning, organizations can process documents at scale while maintaining accuracy, traceability, and long-term reliability across workflows.
Key components and technologies
Traditional rule-based document workflows break down when documents arrive in inconsistent formats, lack standardized structure, or carry meaning that rigid templates cannot capture.
Modern automated document processing systems address this through a layered technology stack – each component targeting a specific gap that rule-based approaches cannot fill. Together, they convert raw files into structured, usable data with minimal human involvement.
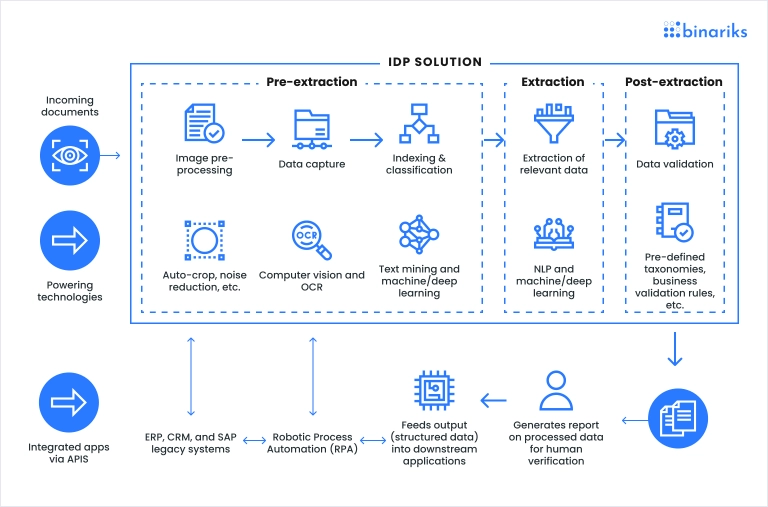
- Machine learning
Machine learning models form the foundation of these systems. They are trained on large document datasets to recognize patterns, classify document types, and extract relevant fields across varying layouts. As models process more real-world data, their performance improves, allowing document pipelines to adapt to format changes without constant reconfiguration.
Deep learning extends this capability by enabling models to recognize complex relationships between visual layout, text structure, and semantic meaning – handling dense or inconsistent documents where simpler ML approaches fall short.
- Computer vision
Computer vision enables systems to interpret visual elements such as tables, stamps, logos, signatures, and layout cues.
It works alongside OCR to improve text recognition quality and supports processing of scanned or image-heavy documents without relying on rigid templates – handling the visual layer that text-based models alone cannot fully address.
- Optical character recognition
OCR converts raw document input, such as scanned pages, printed text, or handwritten forms, into machine-readable text. It serves as the foundational digitization step before classification, extraction, and downstream processing can begin.
- Natural language processing
Natural language processing allows document systems to understand human language in context. This makes it possible to extract names, addresses, dates, clauses, and other meaning-dependent information from unstructured text, which is essential for contracts, reports, and regulatory documents.
Connecting document processing to business workflows
Robotic process automation complements AI components by handling repetitive, rule-based steps surrounding document workflows, such as transferring data between systems or triggering downstream actions.
When combined with AI-driven extraction and classification, RPA closes the loop between document understanding and business action, making document processing a measurable part of broader operational workflows rather than an isolated automation task.
A practical illustration of this architecture is the AI-based insurance underwriting solution built by Binariks, where documents arriving in unstructured formats are automatically extracted, validated, and routed into real-time decision-making workflows – replacing a 15-day manual process.
Use cases of AI document processing
AI-driven document processing is most effective where organizations handle large document volumes, strict compliance requirements, and time-sensitive workflows. Instead of focusing only on task automation, these use cases show how document pipelines become a core operational layer across industries.
Banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI)
In BFSI, document handling sits at the center of customer onboarding, risk assessment, and regulatory reporting. Automating document flows helps reduce processing time while improving data accuracy and auditability across sensitive financial operations.
Common applications include extracting structured data from loan and mortgage applications, automating insurance claims intake , capturing billing and tax information, and routing receipts and supporting documents into downstream pipelines. Companies report measurable improvements after adopting intelligent document processing, reducing manual sorting effort and increasing the quality of financial datasets used for analysis and reporting.
Government
Public-sector organizations manage vast volumes of citizen documents, often across fragmented systems and legacy processes. AI-based document processing helps standardize intake, digitize archives, and accelerate service delivery while maintaining traceability.
Typical scenarios include extracting information from legal and administrative documents, processing public records and census data, verifying applications, and issuing credentials or notifications.
Solutions like those implemented by Mass Vitals demonstrate how document automation can significantly reduce search time, digitize paper-based records, and improve document security in government workflows.
IT and telecom
In IT and telecom, document complexity increases with scale. Customer onboarding, compliance checks, contracts, and infrastructure documentation all generate large amounts of semi-structured data that must be processed accurately.
AI-driven document processing supports automated KYC workflows , extraction of contract and agreement data, management of network equipment documentation, and billing validation. For example, Telecom titan AT&T has combined document intelligence with automation technologies to manage contracts and support uninterrupted customer service at scale.
Healthcare & pharma
Healthcare and life sciences rely heavily on accurate, compliant documentation across clinical, administrative, and regulatory processes. Document automation reduces manual data entry while supporting compliance with healthcare regulations.
Key applications include EHR and clinical documentation automation (e.g., ambient documentation solutions integrated into major EHR workflows to reduce clinician documentation time), credentialing and staff verification, compliance-driven document control, and clinical trial document intelligence.
Take your software to new heights with AI/ML solutions
Examples of document processing implementation
At Binariks, we build document automation projects around real operational constraints: scale, compliance, data quality, and integration with existing enterprise systems. The following cases illustrate how document processing automation moves beyond pilot experiments and becomes a core production capability in complex financial environments.
AI-driven automated fund administration
A global asset management firm faced a fund administration bottleneck : analysts manually validated ~15,000 financial reports per year using Excel checklists with hundreds of regulatory and consistency checks per document. This consumed analyst capacity, increased compliance risk, and blocked scaling.
Binariks designed and delivered a phased intelligent document processing (IDP) pipeline on Microsoft Azure, combining data extraction, AI-driven validation logic, automated workflows, and dashboards for exception handling.
Outcomes:
- 90% faster processing – report validation time reduced by ~90% across annual volumes
- Fewer manual errors – the majority of manual mistakes eliminated through automated validation
- Lower compliance risk – consistent checks applied across documents, improving predictability and control
- Capacity unlocked – analysts shifted from repetitive checklist work to higher-value financial analysis
- Scalable operations – full annual processing volumes supported with predictable accuracy and cost efficiency
AI solution for insurance underwriting
A large insurance provider in the US and UK processed thousands of broker submissions daily, arriving in inconsistent, unstructured formats. Manual extraction and fragmented systems resulted in cycles measured in weeks, inconsistent data quality, and limited leadership visibility.
Binariks implemented an end-to-end AI underwriting document processing platform covering classification, extraction, validation, and decision support. The system combined OCR, NLP, generative AI, and confidence-based routing to handle high document variability while maintaining auditability.
Outcomes:
- Cycle time collapsed – processing times dropped from days to minutes (vs. weeks-long end-to-end cycles previously)
- 80%+ automation – automation exceeded 80% of underwriting document handling
- Underwriter productivity restored – underwriters regained time for true risk assessment (not data wrangling)
- Better decision quality controls – improved appetite enforcement and more consistent data quality
- Executive visibility improved – centralized platform increased reporting accuracy and leadership insight
AI-powered PIL generation
Pharma teams must produce Patient Information Leaflets (PILs) that are accurate, readable, and compliant. Manual PIL creation took 2–3 weeks, was expensive, error-prone, and hard to scale across multiple product launches and frequent label updates.Binariks built an AI + rule-based document automation workflow that transforms SmPC content into structured, patient-friendly PIL sections using controlled mapping logic and automated validation. The solution standardizes formatting and readability rules and adds automated compliance checks to reduce the risk of regulatory rejection.
Outcomes:
- 85% faster cycle time – from 2–3 weeks down to 1–2 days for review and approval
- Higher accuracy and consistency – fewer human errors through structured content mapping
- Compliance baked in – PILs adhere to EU standards (Directive 2001/83/EC) with automated verification to reduce rejection risk
- Scales across launches – supports multiple product rollouts without previous resource constraints
All these examples demonstrate how AI for process documentation enables organizations to treat document flows as part of broader business processes rather than standalone automation tasks. Instead of simply extracting data, these systems enforce structure, validation, and traceability across workflows.
For teams evaluating platforms and vendors, an overview of the best IDP software provides useful context on how these capabilities are packaged and delivered in modern enterprise environments.
10 key AI document processing capabilities
Production-grade document automation platforms are defined by a set of capabilities that determine how reliably they operate under real enterprise conditions. Below is a deeper look at the core capabilities that matter when AI-driven document processing moves beyond pilots and into daily operations.
1. Intelligent document ingestion
Document pipelines can accept inputs from multiple channels, such as email, APIs, cloud storage, scanners, and enterprise applications. Ingestion preserves metadata, source context, and timestamps, which are critical for traceability and downstream validation.
2. Format-agnostic recognition
Using AI document processing technologies, systems handle PDFs, images, spreadsheets, and mixed-format files without relying on rigid templates. This allows organizations to process documents even when layouts change frequently or differ across sources.
3. Context-aware classification
Instead of relying on file names or fixed rules, documents are classified based on layout patterns, semantic cues, and content structure. This enables accurate routing and prioritization even when documents arrive in inconsistent or unexpected formats.
4. Advanced data extraction
Extraction goes beyond static field mapping. Models identify relationships among values, tables, and surrounding text, enabling the reliable capture of complex data such as financial statements, contractual clauses, and multi-page reports.
5. Confidence scoring and validation
Every extracted value is assigned a confidence score and evaluated against business rules or reference data. This step ensures that low-quality or ambiguous data is intercepted before it reaches core systems or reporting layers.
6. Human-in-the-loop review
When confidence thresholds are not met, cases are routed to human reviewers in a targeted way. Feedback from these reviews is captured and reused to improve future accuracy, keeping manual effort focused and incremental.
7. Workflow orchestration
Document processing does not stop at extraction. Systems orchestrate approvals, exception handling, notifications, and downstream actions, allowing documents to actively drive business processes rather than remain passive records.
8. Integration with enterprise systems
Processed data is delivered directly into ERP, CRM, data platforms, or analytics tools through APIs and connectors. This removes manual handoffs and ensures document data becomes immediately usable across operational systems.
9. Continuous learning and adaptation
Through artificial intelligence document processing, models retrain on new data and adapt to evolving document structures, regulatory changes, or business rules. This reduces long-term maintenance effort and preserves accuracy at scale.
10. Auditability and compliance readiness
Every processing step is logged with clear lineage, timestamps, and decision traces. This provides transparency for audits, supports regulatory requirements, and enables organizations to explain how document-driven decisions were made.
A practical example of how these capabilities work together can be seen in an AI-powered fund administration platform, where large volumes of financial reports are processed with consistent accuracy, controlled risk, and full operational traceability.
Core challenges of implementing AI in document processing
Security risks
Converting papers into digital format may cause security concerns, especially BFSI documents, invoices, medical papers, etc. That is why implementing IDP in your business requires additional cybersecurity measures.
Therefore, Binariks can encrypt your data and ensure better security. We also provide access control to improve sensitive data processing.
Data inaccuracy
Correct data input causes accurate data management. Nevertheless, the process of verification often shows errors in the input data. They were caused by manual data input, lousy quality of scanned documents, or handwritten text.
Binariks uses various technologies, such as NLP, OCR, etc., to improve input data quality.
Integration issues
Implementing AI-powered document solutions into existing businesses may be challenging. Some legacy issues must be complied with, as every industry has its rules for managing data.
Binariks provides extensive technical support and constructs integrated systems with high-level compatibility.
Permanent maintenance
IDP requires continuous updating. If you make changes or optimize your usual workflow, you must apply new rules to your intelligent document processing solution. Moreover, AI document processing sometimes requires additional training if the change is significant.
Binariks assists in maintaining intelligent document processing solutions and offers support.
Constant scaling
The amount of data is continuously increasing during business. Thus, it requires the scalability of AI-powered document solutions. Moreover, these volumes of data need to be stored somewhere.
Binariks can implement cloud-based IDP solutions, which help store and manage all data.
Popular AI document processing tools
Below is a concise, implementation-oriented overview of widely used AI document processing platforms. Instead of feature lists, each tool is described by how it is typically used in real systems and what it is best suited for.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is most often used as a modular foundation rather than a single document processing product. Teams combine services like Textract, Lambda, and Step Functions to build custom pipelines for ingestion, extraction, validation, and orchestration. This approach fits organizations that need high scalability, fine-grained control, and deep integration with cloud-native architectures, but it requires engineering effort to assemble and maintain.
ABBYY FlexiCapture
ABBYY FlexiCapture is a mature, enterprise-grade platform focused on high-accuracy OCR and structured document extraction. It is commonly used in finance, shared services, and compliance-heavy environments where document formats are relatively stable and multilingual support is critical. The platform can be deployed on-premise or in the cloud, which is essential for organizations with strict data residency requirements.
Google Document AI
Google Document AI provides pre-trained and custom models for document classification and extraction, tightly integrated into the Google Cloud ecosystem. It is well-suited for teams that want to accelerate time-to-value using managed ML services and human-in-the-loop training. The platform works best when document workflows already rely on Google Cloud infrastructure.
Kofax TotalAgility
Kofax TotalAgility combines document intelligence with workflow automation and decision management. It is often used as part of broader business process automation initiatives, especially in regulated industries. The platform emphasizes end-to-end orchestration, from document capture to downstream actions, rather than standalone extraction.
IBM Datacap
IBM Datacap focuses on enterprise document capture, classification, and data extraction, with strong support for unstructured content and redaction. It is frequently adopted in environments that already use IBM enterprise platforms and require tight governance, security controls, and alignment with compliance requirements.
Comparison table
| Tool | Primary Use Case | Core Capabilities | Scalability | Typical Implementation Effort |
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Custom, high-volume document pipelines | OCR (Textract), layout analysis, orchestration, serverless processing | Very high, elastic | High – requires solution design and engineering |
| ABBYY FlexiCapture | Structured document processing in regulated environments | High-accuracy OCR, rule-based + ML extraction, multilingual support | High for stable formats | Medium – configuration-heavy but less custom coding |
| Google Document AI | Rapid deployment with managed ML models | Pre-trained processors, custom ML, human-in-the-loop training | High within GCP | Medium – faster setup, less control |
| Kofax TotalAgility | End-to-end business process automation | Document capture, extraction, workflow orchestration, decision logic | Medium to high | Medium to high – platform learning curve |
| IBM Datacap | Enterprise capture and governance-focused workflows | Classification, extraction, redaction, unstructured data handling | Medium | Medium – best fit in IBM-centric stacks |
In practice, there is no universal “best” tool for document processing. The right choice depends on how deeply document workflows must integrate with existing systems, how much flexibility is required to handle format variability, and which compliance or governance constraints apply.
For most enterprises, long-term success comes from aligning the tool’s architectural model with their broader data and process strategy rather than selecting based solely on individual features.
Summary
AI-based document processing delivers real value only when it is built as part of an end-to-end operational system, not as an isolated automation. Architecture, data quality, integration, and long-term adaptability are what separate production-ready solutions from short-lived pilots.
Binariks helps organizations design and implement document processing systems that work at enterprise scale, with a focus on reliability, compliance, and measurable outcomes. If you’re planning to modernize document workflows or scale existing automation, get in touch to discuss how we can support your implementation.
FAQ
Share

